祁连山排露沟流域吉拉柳灌木林土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P619.2 文献标识码:A doi:10.13601/j.issn.1005—5215.2025.04.010
Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil Carbon,Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Salix gilashanica Shrub Forests of Pailugou Basin in Qilian Mountains
He Yongyan,Zeng Wanqi,Wu Longqing (Academy of Water Resources Conservation Forests in Qilian Mountains of Gansu Province,Zhangye 7340o,China)
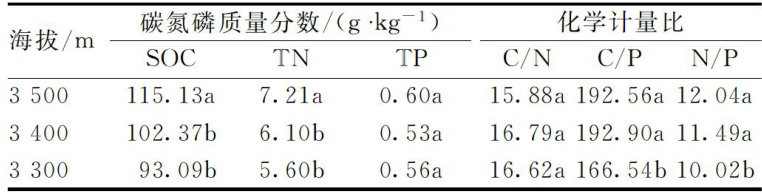
AbstractThe stoichiometric characteristics and driving mechanism of soil carbon (C),nitrogen (N)and phosphorus (P)in Salix gilashanica shrub forests of Pailugou Basin in Qilian Mountains were revealed,which could provide scientific basis for regional ecosystem management. The Salix gilashanica shrub forests at an altitude of 3300- (204 3500m of Pailugou Basin in Qilian Mountains were taken as the objects.The mass fractions of soil organic carbon (SOC),total nitrogen(TN)and total phosphorus (TP)in Salix gilashanica shrub forests at diferent altitudes were measured by stratified sampling.The C/N,C/Pand N/P ratios were analyzed by stoichiometry,and their vertical distribution and correlation were analyzed.Theresults showedthatthe mass fraction ofSOCand TN in soilincreased significantly with the increase of altitude. The SOC in 0-10cm soil layer at 3500m altitude was 146.74g⋅ (204号 kg-1 ,and TN was 8.15g⋅kg-1 ,showing significant “surface aggregation”. There was no significant difference in TP mass fraction (0.52-0.61g⋅kg-1 )among different altitudes and soil layers. C/P and N/P increased significantly with the increase of altitude,while C/N changed little. C/N,C/P and N/P in 0-10cm soil layer were significantly higher than those in deep layer,while C/P and N/P in deep layer >30-40 cm decreased due to leaching or microbial activity. SOC and TN were significantly positively correlated with C/P and N/P , while TP was weakly corelated with other parameters.The accumulation of soil carbon and nitrogen in Salix gilashanica shrub forests in QilianMountains isregulated byaltitude gradient,and thelack of phosphorus availabilitymay become thekey factor of nutrient limitation in ecosystem.The stoichiometric characteristics of surface soil are sensitive to altitudechange,
whilethedeepsoil tendsto bestable.
Key words Pailugou Basin in Qilian Mountains;Salix gilashanica ;soil carbon (C),nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P);stoichiometric ratios
生态化学计量学通过研究碳(C)、氮(N)、磷(P)等元素的平衡关系[1],为揭示生态系统的养分循环和植物适应策略提供了重要理论框架。(剩余8708字)