高盐渍区不同盐分矿井水灌溉下怪柳的响应机制与适应性

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S728.5;S731.6 文献标识码:A doi:10.13601/j.issn.1005—5215.2025.04.005
Response Mechanisms and Adaptability of Tamarix chinensis to Different Salinities of Mine Water Irrigation in High-salt Area:
Chen Junfu1'²,Xu Hailiang1.2*,Tong Zewen³,Miao Zhiguo4,Zhang Qian1,Li Xihong1 (1. College of Forestry and Landscape Architecture,Xinjiang Agricultural University,Urumqi 83oo52,China;
2. Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Urumqi 8300l1,China;
3. Xuzhou Coal Mining Group Hami Energy DevelopmentCo.,Ltd.,Hami 839l21,China;
4.Land Consolidation Center of Hami City,Hami 83oo99,China)
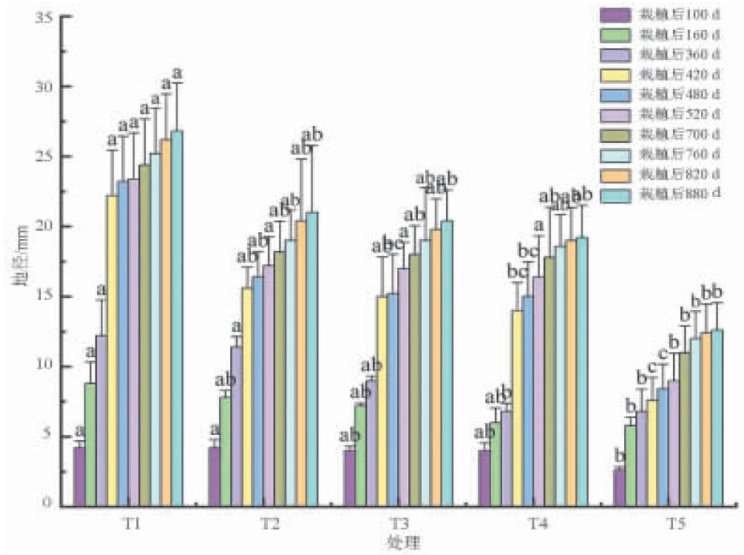
AbstractTaking the high-salt areasofHami in Xinjiang as theexperimental sites,the mine water with differentsalt gradients (0,4,8,12,16g⋅L-1) ) was set to irrigate the Tamarix chinensis forest,and the indexes of ground diameter,plant height,crown width and new branch lengthof Tamarix chinensis were measured.Combined with variance analysis and least significant diference method (LSD)test,the growth response mechanisms and adaptability of Tamarix chinensis in extreme saline environment were explored.Theresults showed that salt significantly inhibited the growth of Tamarix chinensis ,but the plants stillshowed gradient adaptability. Under clear water irigation (0g (204号 L-1 ),the indexes of Tamarix chinensis were the best,and the inhibitory effect of salt⩾8g⋅L-1 on ground diameter,plant height and crown width was significantly enhanced ( P<0.05 . The salt mass concentration was negativelycorrelated with ground diameter and exponentiallycorelated with crown width inhibition,while the new branch length was close to the control group under low salt (4g⋅L-1) . The growth was the lowest under 16g⋅L-1 (204号 high salt treatment,and the long-term inhibitory effect of high salt on plant height was significant ( P<0.05 ),but it could still survive.
Key WordsTamarix chinensis ;salinity stress;mine water irigation;growth response;high-salt area怪柳(Tamarixchinensis)为怪柳科(Tamari- caceae)怪柳属一种典型的耐盐碱、耐干旱且耐水淹植物,常见于温带海滨河畔等处湿润盐碱地,有很强的抗盐碱能力,能在含盐碱 0.5%~1.0% 的盐碱地上生长,是改造盐碱地的优良树种[1-2]
高盐渍化土壤是全球干旱区生态修复的难点问题。(剩余7050字)