祁连山典型流域青海云杉林土壤磷研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S714 文献标识码:A doi:10.13601/j.issn.1005—5215.2025.04.004
Study on Soil Phosphorus Picea crassifolia Forest Typical shed
Miao 1, , 1, 1, ² (1.Academy Provce, ,Cha; 2.Ganzhou District works Authority, 734ooo,Cha)
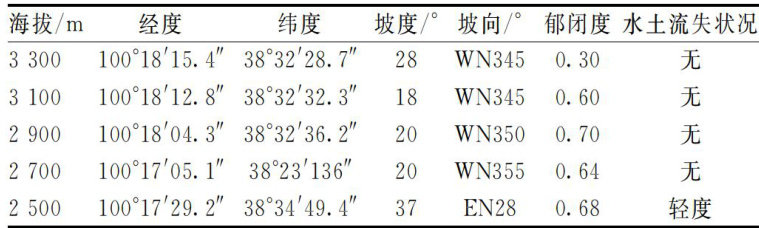
AbstractIn order to reveal thevertical distribution pattern,altitude differentiation characteristics soil phosphorus and the fluence mechanism organic matter on the transformation phosphorus forms Picea crassifolia forest the typical watershed ,the Picea crasifolia forest Dayekou Bas was taken as the research object,and the sample plots were set up at an altitude gradient 2 500- (2 3300m . The soil prile was excavated and the soil samples were collected layers for the determation total phosphorus,available phosphorus and organic matter. The data were analyzed by nonlear regression and Pearson corelation test. The results showed that the massfraction total phosphorus decreased with the crease soil depth at low and medium altitudes ( 2500-2900m ),and the deep soil at 3100m was enriched phosphorus due to weatherg or meralization.Available phosphorus only decreased with thedeepeng soil layer atan altitude 2700m ,and there was no significant law at other altitudes. The mass fraction total phosphorus creased first and then decreased with the crease altitude,and reached the peak at 2900m . The available phosphorus decreased with the crease altitude,and the mass fraction available phosphorus at 3 300m was slightly higher than that at 3100m . Available phosphorus was significantly negatively correlated with organic matter,while total phosphorus was not significantly correlated with organic matter. Hydrothermal conditions at an altitude 2900m (204 are mostconducive to total phosphorus accumulation,and available phosphorus is reducd at high altitudes due to low temperature and organic matter adsorption.
Key words Dayekou Bas ;Picea crassifolia forest;soil prile;soil phosphorus磷是陆地生态系统生产力的关键限制性养分元 素之一,其在生物地球化学循环过程直接影响森林生态系统的结构和功能[1-2]。(剩余7394字)