基于机器学习算法构建老年重症病人静脉血栓栓塞症风险预测模型

打开文本图片集
Development of risk prediction model for venous thromboembolism in elderlycriticallyill patient based on machine learning
JIN Jiel, XU Qing²,LU Jie', ZHAO Jiayue',ZHANG Qing1,KONG Yang1* , XU Hongmeil* 1.Binzhou Medical Colege,Shandong 25660o China;2.Binzhou Medical College Yantai Affiliated Hospital *Corresponding AuthorKONG Yang,E-mail: kongyang@ bzmc.edu.cn; XU Hongmei,E-mail: hmx58@163.com
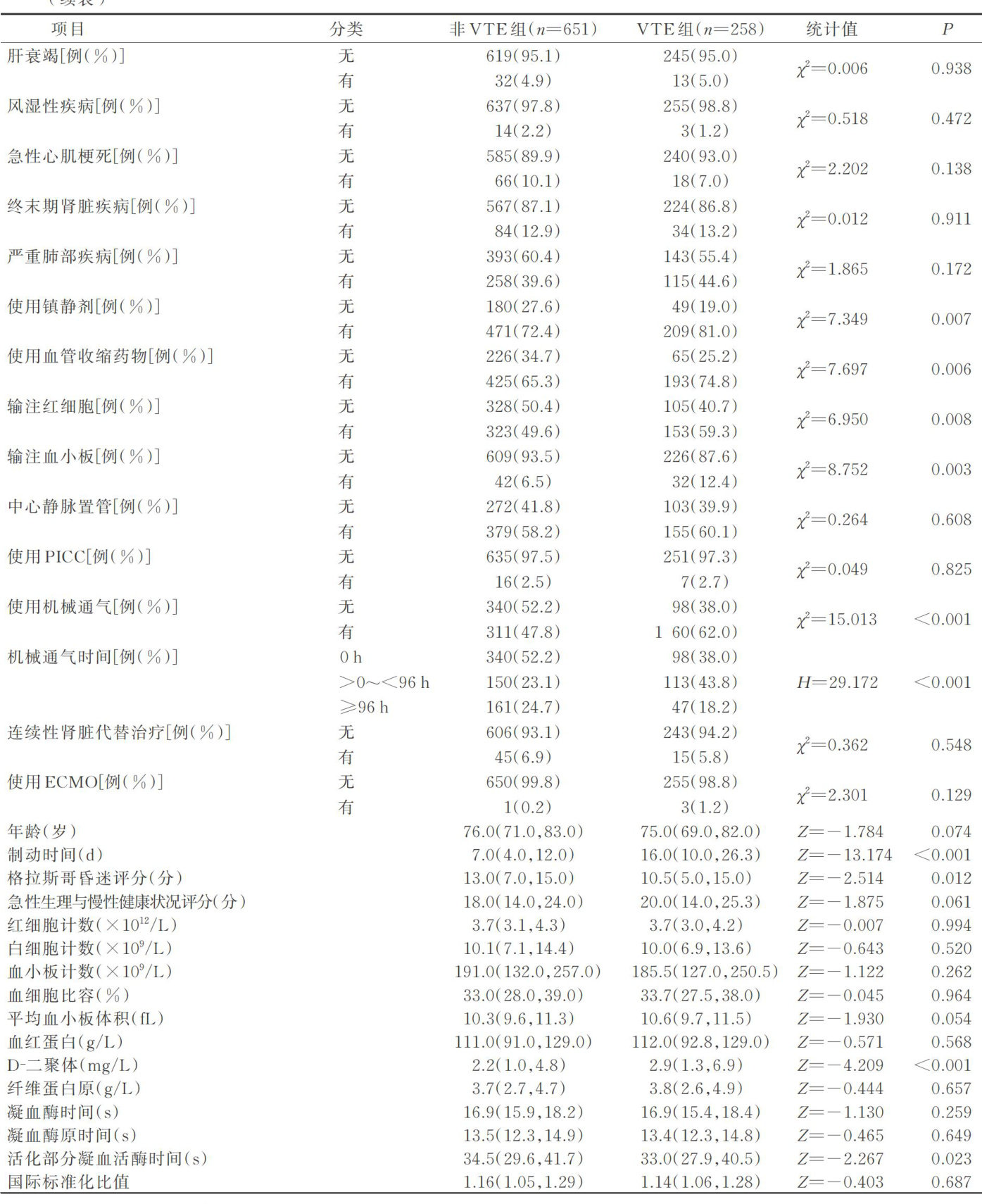
AbstractObjective:Todeveloprisk prediction modelforvenous thromboembolism(VTE)inelderlycriticalyillpatients basedon machineleatotaflillltoeUtee hospitalsinShandongprovincewereselectedasstudysubjectsfromJanuary2O2OtoJune2O23.Andclinicaldatawerecolected.The patients wererandomlydivided intotrainigset36cases)andvalidationset273cases)at7:3ratio.heocurrenceofVTEduringICU hospitalizationwasused as theoutcome variable.Predictionmodels wereconstructed using 4machinelearing,namelyrandomforest, extremegradientbosting,supportvectormachines,andgadientbostigdecision tre.Modelperformancewas evaluatedusingmetrs suchasareaunderthecure(AUC)ofreceiveoperatorcharacteristicandBrierscoreandteoptialmodelwasselected.Inteeability analysisfthebestperformingmodelasconductedusingteSHAPlgorithmResults:Amongthe909elderlyrticallillpatients58 developed VTE, with incidence of 28.4% .Among the 4 models,the random forest achieved the higher AUC(O.8O3),accuracy(0.733), senitivity(.662),ndspecificiy(0.76),alongiththelowestBrierScore(O.171).onclusions:TheriskpredictionmodelforE inelderlycriallyillpatientsdevelopedbasedonandomforestdemonstratedstrongpredictiveperformance.Itouldproideeference for optimizing VTE management in elderly critically ill patients.
Keywordsmachine learming; elderly;critical illess;venous thromboembolism; prediction model; random forest
doi:10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2025.14.002
静脉血栓栓塞症(venousthromboembolism,VTE)包括深静脉血栓形成(deepvenousthrombosis,DVT)和肺栓塞(pulmonarythromboembolism,PE),是仅次于心肌梗死和脑卒中的第三大常见心血管疾病,具有发病率高、病死率高以及复发率高的特点,是重症监护室(intensivecareunit,ICU)病人常见的并发症之一[1-2]。(剩余11466字)