玫瑰纯露的提取工艺研究及其抗氧化能力分析
打开文本图片集
中图分类号TQ658 文献标识码A 文章编号 1007-7731(2025)16-0089-04
DOI号10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2025.16.019
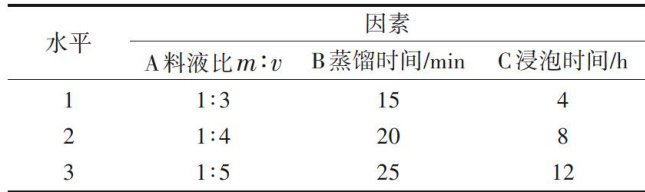
AbstractInthis experiment,biter rose petals were used as experimental material,water was usedas the solvent, and steamdistilation was used toextractrose hydrosol.Single-factor experiments (Asolid-liquidratio,Bdistilltion time,C soaking time)andorthogonal experiments were used todetermine theoptimal combinationofthese factors.The sensory score,DPPHfree radical scavenging rate,ABTS free radical scavenging rate of the combination were measured todetermine the optimal extraction process of rose hydrosol.The single-factor experiment resultsshowed that the optimal ratio m:v for extracting rose hydrosol is 1:4 ,the optimal distillation time is 2O min,and the optimal soaking timeforpetals is8h.Theorthogonal experimentresultsshowed thattheprimaryand secondary factorsaffecting the extraction of rose hydrosol in sequence were the solid-liquid ratio,distilation time,soaking time. The score of A2B2C3 (204 (theratio of material toliquid m⋅v is 1:4 ,distillation time 2O min,soaking time 12h) was the highest,reaching 8.2 points.The DPPH free radical scavenging rate and ABTS fre radical scavenging rateof the rose hydrosol extracted from it were 66.27% and 66.78% respectively, indicating a strong antioxidant capacity. In conclusion, the optimal process condition for extracting rose hydrosol is a material-to-liquid ratio of m⋅v of 1:4 ,a distillation time of 20 min,and a petal soaking time of 12h .This article provides a reference for the comprehensive utilization of rose hydrosol resources.
Keywordsrose hydrosol; extraction process;antioxidant capacity; sensory evaluation
玫瑰属蔷薇科蔷薇属落叶灌木或乔木,花瓣呈倒卵形,多为重瓣、半重瓣1。(剩余5378字)