钠盐强化表面活性剂清洗石油污染土壤的性能及其作用机制

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S143.1 文献标志码:A
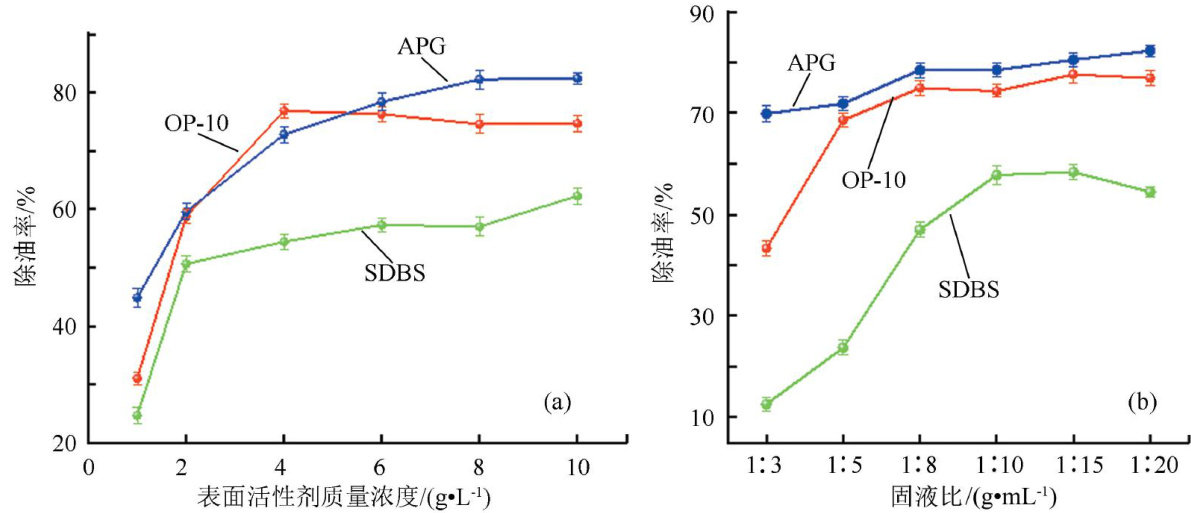
Abstract:Thecleaning performanceofthree surfactants,sodiumdodecylbenzene sulfonate(SDBS),octylphenolpolyoxyethyleneether(OP-10)andalkylpolyglycoside(APG),wasstudiedforsimulatedoil-contaminatedsoil withoilremovalrate as the idex.Under the most suitable cleaning conditions,theoil removal rates of APG,OP-1O and SDBS were 77.5% , 71.3% and 58.6% respectively. The effects of four sodium salt additives, namely,sodium silicate,sodium carbonate,sodium phosphateand sodium humate,onthe cleaning performanceof surfactants were investigated,and their efects on the microscopic properties of surfactant solutions were further explored to reveal their mechanismofaction.Results show that sodiumsalts exhibit synergistic effectonsurfactantcleaning,butithasacertain matching.The matchingof sodium silicate with SDBS and OP-10 is better,and the matching of sodium phosphate with APG is better.Underthe best washing conditions, the oil removal rates reach 88.9% , 85.3% and 72.0% with APG-sodium phosphate, OP-10-sodium silicate,and SDBS-sodiumsilicate,respectively.Aftertheaditionofadditives,byreducing thesurface tensionandcritical micellconcentration of the solution,reducing theoil-waterinterfacial tensio,increasing thedynamicaveragediameterof the miceles,andimprovingthewetabityofthecontaminatedsoil,thesynergisticstrengtheningofthesurfactanttoexerttheefectofshrinkage and solubilization,thereby improving the cleaning performance of the oil-contaminated soil.
Keywords:surfactant;petroleum-contaminated soil;soil cleaningand remediation;sodiumsaltadditives;mechanisr
随着石油工业的发展,石油在开采、加工、运输等过程中带来的土壤污染愈来愈严重[1]。(剩余11984字)