热流固-损伤多场耦合作用下干热岩水力压裂特征数值模拟

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TK521 文献标志码:A
Abstract:Hydraulic fracturing serves asacritical pathwayfortheeficient developmentofdryhotrockresources,and itscore processinvolves theinjectionoflowtemperatureandhigh-pressrefluidsintohigh-temperature,hig-stresrock foratios,in which coldshock-induced thermal stresscan playavitalroleinfracture initiationand propagationwithinthehotdryrock. However,theevolution characteristicsof stre/temperature and fracturepropagation patterns inhigh-temperaturerock matrix undercoupled thermo-stressinteractionsremainunclear.Inthisstudy,a thermo-hydro-mechanical-damagecoupledfracture propagationdelwastablised,corporatingwelloresresssuperpositioneects,rocktero-poroelasticespons,ela tic-britlefailurecriteriaandpermeability-porosityvariationswithmatrixdamage.Themodel'saccuracywasvalidatedhroughcomparisons withtheresultsofanalyticalsolutions forwelborecoolingandfracturepropagation.Numerical simulationsunder varyinggeothermalstressconditionsandfluid injection temperaturerevealthat,duringfracture initiation,trong thermalstresses nearthe welborecan promotemulti-directional fractureextension,whilethesubsequentpropagation becomes increasingly dominatedbyin-situstressdistribution,causingfracturereorientationtowards themaximum principal stress direction,whilethe variationof temperatureislocalizednearthewelloreregion.Largertemperaturediferentialscanenhancethermal stresses,reduce nitiationpressuresandfaciliatethedevelopment ofcomplexfracture networks.Smaller in-situ stressdiferetials(under constantmaximum principal stress)can weaken thecontrolof fracture initiation/propagationdirections bystressfield,promting the formation of complex fracture networks while inducing greater stress perturbations.
Keywords:hotdryrock;hydraulicfracturing;thermal-hydraulic-mechanical-damagecoupling model;thermalstress;in-situdifferential stress ; breakdown pressure; fracture propagation patterns
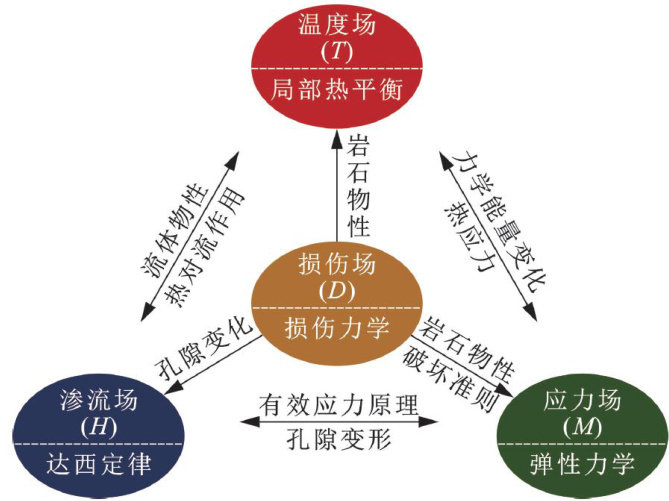
干热岩(hot dryrock,HDR)地热资源储量大、分布广,是一种极具潜力的可再生清洁能源。(剩余14898字)