盾构隧道穿越岩溶区注桨加固对地层及管片的影响

打开文本图片集
Abstract:TheXiaoshui shieldtunelingsectionoftheGuangxi branch linealong the Xinjiangcoal-to-gaspipelineforexternal transmission,locatedinthekarst-developedregionofYongzhou City,HunanProvince,employsslurrybalanceshieldtuneling technologytotraversestronglydevelopedarststrata(karstandform).Byfocusingonfourheterogeneouskarstcaves(fulfilled, partillyileandfild)istrbutedoundtuel,dimensioalfuddoupligumercalodelwaabld basedontheZK1ltypicalcross-section.Theinflunce mechanismsof thespatialdistributionofkarstcavesonsuroundingrock stabilityandteefectivensofgoutingeinforementweresystematicallyinvestigatedResultsindicatetatinuntreatedsenaios, theplasticzosofrckslbsetwenas1/andtheteloeintercoted,adngtoiumselemenof0.49m anda peak segment stress of1.76 MPa.Aftercement mortarreinforcement,te maximum ground settlementdecreases by 22.4%(0.38mm ) segment stress reduces by 4.6%\~8.2 % ,and plastic zone volume diminishes by 58.7% . The findings reveal the progressive failure mechanismofsuroundingrockinkarst shieldtunnelsand proposeatreatmentthresholdforkarstcaves basedonplasticzone conectivitycriteria.Thisresearchprovidesafluid-solidcouplinganalysismethodandprocessoptimizationframewrkforriskontrol in the Xiaoshui Tunnel and similar engineering projects.
Keywords:shieldtunnel; karststrata;numericalsimulation;suroundingrockinstability;plasticzone;groutingreinforcement
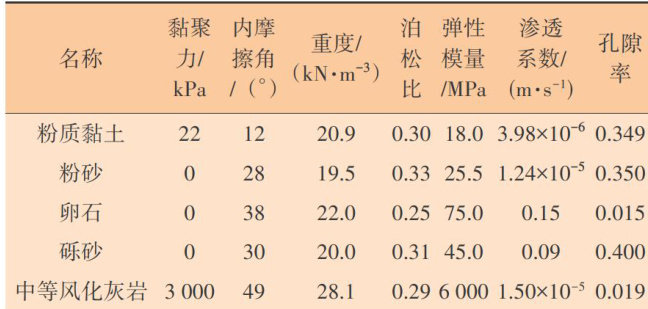
在我国岩溶发育地区,盾构隧道工程建设常面临复杂地质挑战。(剩余7758字)