南美斑潜蝇不同种群生物学特征的比较分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S433 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1671-4652(2025)02-0077-06
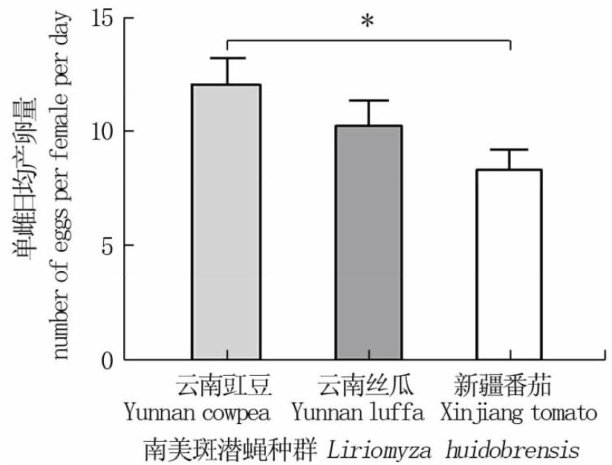
ABSTRACT:The invasive leaf miner Liriomyza huidobrensis is a notorious pest of vegetables and flowers in China. Understanding the biological performanceof diferent populationsofL.huidobrensis provides thefoundation for clarifyingits adaptability tonovelenvironments.In this study,various biologicalcharacteristics,including egg production,egg hatching rate,pupation rate,eclosion rate,and pupal morphology,were assessed within threeL.huidobrensis populations: Yunan cowpea,Yunnan luffa,and Xinjiang tomato.The results showed thatthe number of eggs and pupal length of L.huidobrensis on tomatoes in Xinjiang were significantly lower than thosein the Yunnan cowpea population,while its emergence rate and developmentalduration were significantlyhigher than those in the Yunnan luffa population. However, there was no significant diference in egg hatching rate,pupation rate,pupal width,and pupal weight among the three populations ofL.huidobrensis.This studyfound that bothhost plants and geographic factors can potentiallyafect the re productiveand other biological characteristicsofL.huidobrensis populations.Theresults provideavital theoretical basis for understanding the invasion and environmental adaptationofL.huidobrensis,as wellasfor implementing environmentally friendly control strategies.
KEY WORDS: Liriomyza huidobrensis ; different populations; biological characteristics
外来人侵昆虫可对人侵地生态系统及生物多样性造成严重威胁,反之,人侵地的地理、气候等环境因素亦会影响人侵昆虫的生殖与适应性,从而决定人侵昆虫对其适合度与定殖情况[2-3]。(剩余9588字)