桃采后腐烂病的病原菌鉴定及生物防治研究

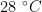
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S436.61 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1671-4652(2025)02-0066-10
ABSTRACT: In order toclarify the pathogen species of postharvest peach and carry out biological control of peach postharvestrot.Inthis study,the fresh and healthy peach fruits from Jiangsu and Shandong provinces were stored at room temperature,andthe pathogen isolation,pathogenicity determinationand molecular biology identificationof rotten fruits were carried out.The efectof Bacillus licheniformis W10on the preservation of postharvest peach fruits was investigated.Theresults showed thata totalof16 speciesoffungi were isolated from the roting peach fruits,among which Diaportheeres,Botryosphaeriadothidea,Alternariaalternata and Diaportheamygdali had higher frequencyin peach fruits fromdifferenthabitats.ThepathogenicityofDiaportheeres,Botryosphaeriadothidea,Diaporthelongicoll,Diaporthe phaseolorum,Neopestalotiopsis rosae,Colletotrichumaenigma,Diaportheceleris,Diaportheamygdali,Botrytis cine rea and Aspergillus flaus was strong or relatively strong. The preservation tests showed that Bacillus licheniformis W10 bacterial suspension treatment could significantly reduce therotrateof peach fruits during storage,and had no ffect on weight loss and solublesolids contentof peach fruits during storage.Theresults provideareferenceforthecontrolof postharvest peach diseases and the further application of biocontrol bacterium W1O strain.
KEY WORDS: peach; postharvest diseases; pathogenic identification; Bacilus licheniformis ; preservation
桃[Prunus persica(L.)Batsch]是蔷薇科(Rosaceae)李属(Prunus)桃亚属(Amygdalus)植物。(剩余16109字)