湖羊耐热性的评价及生理生化指标、免疫功能的检测与分析

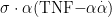
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S826 文献标识码:A 文章编码:1005-8567(2025)04-0008-09
Abstract:Thepurpose of this experimentwas to explore the changes in physiological indices,serum biochemical indices and immune function of Hu sheep with diferent heat tolerance,and to provide reference for analyzing theheattolerance mechanismofHusheepandforulatingstrategiestoallviatehatstressofseep.FromJulytoAugust 20,undertheconditionof anaverageTH(Temperature-HumidityIndex)of 85.5,atotalof81lmultiparous,non-pregnantewes withconsistentparity(allhavinggivenbirthtwice),goodhealthstatus,andidenticalfeeding managementwereselectedandraised collctivelyinasingleshedIndicatorssuchasrespiratoryate,rectaltemperature,andheartrate were measured.Usingprncipal component analysis and membership function analysis,heat-resistant (HR)Hu sheep ( n=30 )and heat-sensitive (HS) Hu sheep ( n=30 )wereidentified.Theresultsshowedthattherespiratory frequency,rectal temperatureand heartrateof Husheep in HS group were significantly higher than those in HR group ( P<0.01 ).WBC and HGB in the blood routine of Hu sheep in HR group were significantly higher than those in HS group ( P<0.01 ),and LYM was significantly higher than that in HS group ( P<0.05 ). The contents of serum HSP7O and HSP9O in HR group were significantly higher than those in HS group ( P<0.01 ). The contents of T3, T4 and COR in HR group were significantly higher than those in HS group ( P<0.01 ).The concentrations of TNF- α ,IL 1β and IL-6 in HR group were also significantly higher than those in HS group( P<0.01 ).In conclusion,compared with HS Hu sheep,HR Hu sheep exhibit stronger heat stress resistance and immune capacity.
Keywords:Heat stress;Heatresistance;Hushep;Physiological indicators;Serumbiochemical indexes;Immunefunction
热应激是动物因无法通过正常生理调节释放体内积热以维持恒温而引发的系列生理与行为反应1]。(剩余12877字)