柴汶河硅藻水华氮磷驱动特征、空间分异与分区治理研究

打开文本图片集
Abstract:Toservethemajorstrategyofecological protectionintheYellowRiver Basin,andaimingattheaquaticecological risksintributariescausedbyitrogenandphosphoruspolution,thisstudytakestheChaiwenRiver,atypicaltributaryintelower reachesoftheYelowRiver,astheresearchobject.Through monthlymonitoringof7sections inthemainriverchannelfrom2023 to2024,combiedwithphytoplanktoncommunityidentificationandwaterqualityparameteranalysis,itrevealsthattheChaiwen Riverexhibitsa"nitroge-dominatedandphosphorus-limited"nutrientpattem:Algaldensityisweaklycorelatedwithtotal nitrogen (r=0.420 P<0.001 ),and negatively correlated with total phosphorus (r=-0.289) ).During the dry season,diatom blooms reach a moderate level (peak value of 3.74×107 cells/L, with Cyclotella accounting for 95.13% ).The spatiotemporal differences in nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients are significant: Total nitrogen (2.7-39.5mg/L) is thehighest in winter and downstream,mainly influenced by sewage discharge and algal metabolism; total phosphorus (0.01-1.3mg/L) isrelatively high in the middle and upper reaches as wellas in spring and summer,mainly due to aquaculture wastewater discharge;ammonia nitrogen (peak value of 3.6mg/L at CW3) and nitrate nitrogen (peak value of 11.57mg/L atCW7) are driven by agricultural and industrial wastewaterdischargeandgroundwaterrecharge,respectively.Basedonthesefindings,a"zoning-grading-coordination" goverance approach isproposed,suppementedbycrossrgionalcological waterreplenishment during thedryseasonThis providesatechnicalparadigmformeetingthebasinassessmenttargetsduringShandongProvince's14thFive-YearPlanperiod and for implementing targeted pollution control in the Yelow River tributaries.
Keywords:Yelow River Basin; ChaiwenRiver;diatomalgal bloom; cyclotella; nitrogenand phosphorus nutrients
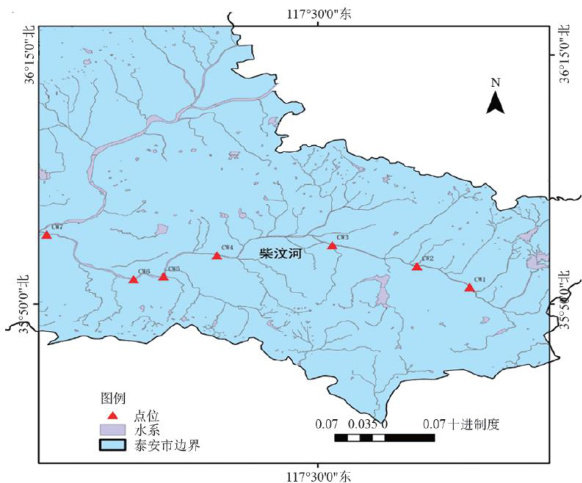
在水生生态系统中,硅藻是不可或缺的一部分,对维持水域的生态平衡和水质状况起到了重要的指示作用,在河流和湖泊的水环境监测及生态健康评估至关重要[1-3]。(剩余14494字)