碳点对四环素类抗生素的荧光检测

打开文本图片集
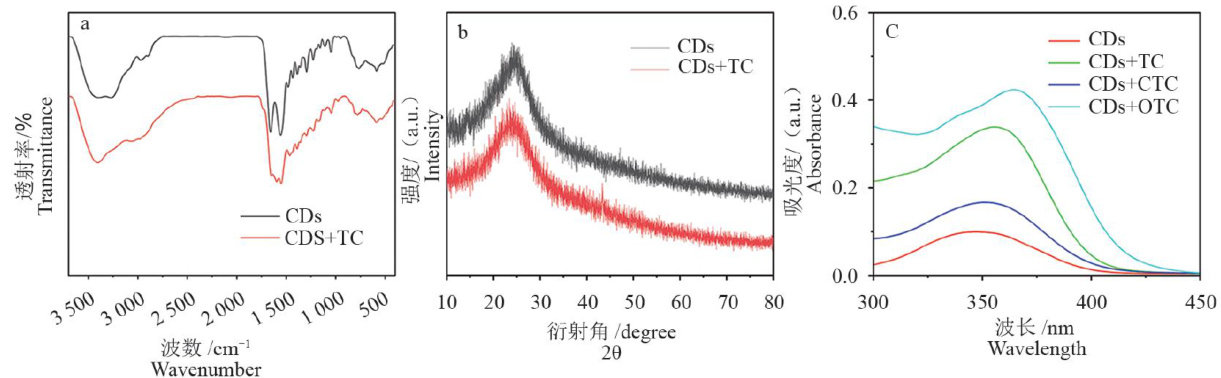
Abstract:Tetracyclineantibiotics (TCs)areacommonlyused classofbroad-spectrum antibiotics.Due to their broadspectrumantibacterial properties,theyare widely applied in multiple industries such as medicaltreatment and animal husbandry.However,excessive usecan lead to the residue of TCs,posing a serious threat to the ecological environment and human health.Therefore,itisof great significance to developa simple,efficient,rapid,and sensitive method to detect TCs residues for monitoring the environment and food safety.Fluorescence sensing methods have the advantages of obvious phenomena, high sensitivity and convenient operation.This paper synthesizes carbon dots by one-step hydrothermal method with citricacid and ethylenediamine as precursors.It characterizes the carbon dots by infrared spectroscopy,ultraviolet spectroscopy,powder X-ray difraction,and fluorescence spectroscopy. Their optimal excitation wavelength is determined as 350nm ,with the maximum emission wavelength of 450nm ,exhibiting blue fluorescence.Moreover, this paper employs carbon dots for fluorescence detection of tetracycline,chlortetracycline,and oxytetracycline.The blue fluorescence gradually quenches when carbon dots interact with TCs.Within the range of 0-250μM ,the detection limits of tetracycline, chlortetracycline,and oxytetracycline are 720nM,747nM ,and 765nM ,respectively.This paper also investigates the optimal detection conditions and the influence of possible interfering ions on TCs detection.The results show that the carbon dots exhibit significant selectivity for TCs.
Keywords:Tetracycline antibiotics; carbon dots; fluorescence detection;high sensitivity; high selectivity
四环素类抗生素(TCs)是环境中常见的污染物之一,在自然水系、土壤中都可检测到以TCs为主的残留物[1]。(剩余8328字)