含软弱夹层边坡稳定性及抗滑桩支护效果研究

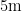
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TU457 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1005-8249(2025)02-0085-06
DOI:10.19860/j.cnki.issn1005- 8249.2025.02.015
Abstract:To studythestabilityofslopes containing weak interlayers,basedonthetreatmentofalandslideinacertainwater conservacy project,thefactorsafecting slope stabilityandtheefectivenessofanti slippiletreatment were studied.Abaqus software wasused to modelandcalculate theimpactofchanges inanti slippileparametersonslopestability.Theresults show thatthedisplacementoftheupperpartof heslopeisrelativelylargeamong thevariousstepsoftheslope.Inthedepthdirection of the slope,thereisacertainfluctuationinthedisplacementofeach step.Thedisplacementatadepthof2O.2misrelatively large,but the cumulative displacement is always within a smal range ( , ± 1 0 m m ). After being supported by anti slip piles,the displacement of theslope graduall tends to stabilize;Rainfallandengineringactivitiescan causedisturbance totheslope, acceleratingitsinstability.However,anti slippileshaveagoodefectonreinforcingtheslope,andthecumulativedisplacement values arestable withinthecontrolrange;Through numerical simulationoptimizationofanti slippiledesign,itwas found that themosteconomical andreasonablesolutionis whentheanti slippileis locatedat thesecond step,with a pilelengthof 2 3 . 4 m (20 and a pile spacing of
Key words:soft interbedded strata;field monitoring;slope stability;slip-resistant pile design optimization
0 引言
我国幅员辽阔,地质构造具有显著的区域差异性,其中滑坡灾害作为最具破坏力的地质灾害类型之一,其突发性强、致灾链复杂的特点,往往伴随着重大人员伤亡、基础设施损毁和巨额经济损失,对社会经济发展构成严峻挑战[1-2]。(剩余6037字)