1株耐碳青霉烯类鲍曼不动杆菌BM5的生物学特征及基因组序列分析

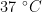
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R378 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1671-4652(2025)01-0079-1
DOI:10.16872/j.cnki.1671-4652.2025.01.010
ABSTRACT:Inorder to explore thegenomeand molecularbiological characteristicsof Acinetobacter baumanni,aclinically isolated pathogen was selectedas the target strain and named BM5.The drug resistance of Acinetobacterbaumanii was analyzed by drug sensitivity test,its genome wasanalyzedby high-throughput sequencing,its multi-sitesequence typing (MLST),drug resistance genes and virulence genes were analyzed and predicted by relevant databases and bioinformatics methods,and its evolutionary correlation withother Acinetobacterbaumammi strains was determined byanaly zing and comparing genomic sequence similarity.Theresults showed thatthe whole genome was 3990385 bp circular DNA with GC content of 38.9% . The strain also contained two ring plasmids (72 258 and 8 731 bp in length). The MLST type of the bacterium was ST2,carrng 85 drug resistance genes and including carbapenem resistance genes (96.63% ),83virulence genes and 5 prophages.Therefore,the bacterium may acquire and maintain its multi-drug resistance and complex pathogenicity through multiple pathways.In conclusion,the genomic characteristics of the new carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumanni BM5 were analyzed,which willaya foundationfor further researchon the mechanism of drug resistance and pathogenic mechanism of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.
KEYWORDS:carbapenem resistant;Acinetobacter baumamii;whole genome sequencing;drug resistance gene;virulence genc
长期以来抗生素在控制和治疗细菌感染性疾病方面发挥着重要作用,但随着抗生素的滥用,细菌进化出各种耐药机制,对多种抗生素产生耐药性,多耐药菌及全耐药菌的出现及流行,成为全人类健康的重要威胁之一[1]。(剩余17614字)