中国绿豆种质资源营养品质多样性及其地理环境关联性分析

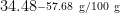
打开文本图片集
Abstract: In order to enhance the quality of mung bean varieties and facilitate precision breeding,the nutritional quality diversity of 528 mung bean samples from 16 regions in China was analyzed,follwed by comprehensive evaluation using coefficient of variation,cluster analysis and correlation analysis.The study revealed substantial compositional variation in contents of protein,starch,fat,total polyphenol and total flavonoid that were 16.14-29.19g/100g , , 0.67-1.34g/100g , 1.63-6.78mg GAE/g and
0.59-2.83mgRE/g ,respectively.The coefficient of variation ( (CV) ranged from 4.49% to 22.98% ,indicating robust genetic diversity.Geographic clustering identified distinct regional nutritional profiles.Accessions from Hubei province were characterized by elevated protein content,accessons from Jilin province were characterized by high starch accumulation,accessions from Shandong province were characterized by increased fatcontent,accessions from Chongqing were characterized by accumulated higher polyphenols,while accessions from Shaanxi province were mainly characterized by higher flavonoids. Correlation analysis indicated positive trends between longitude and protein content,starch content and total flavonoids content,while total polyphenols content showed a negative correlation with longitude and fat content was negatively corrlated with altitude.These findings provide critical insights for precision breeding,optimized germplasm utilization,and value chain development in mung bean production systems.
Key words : mung bean;nutritional quality;variation analysis ; cluster analysis ; environmental factors
绿豆是我国传统豆类之一,属于一年生可食用豆类作物,在我国广泛种植,年总产量接近100万吨,居世界第一[1]。(剩余15127字)