普通菜豆苗期耐旱性鉴定

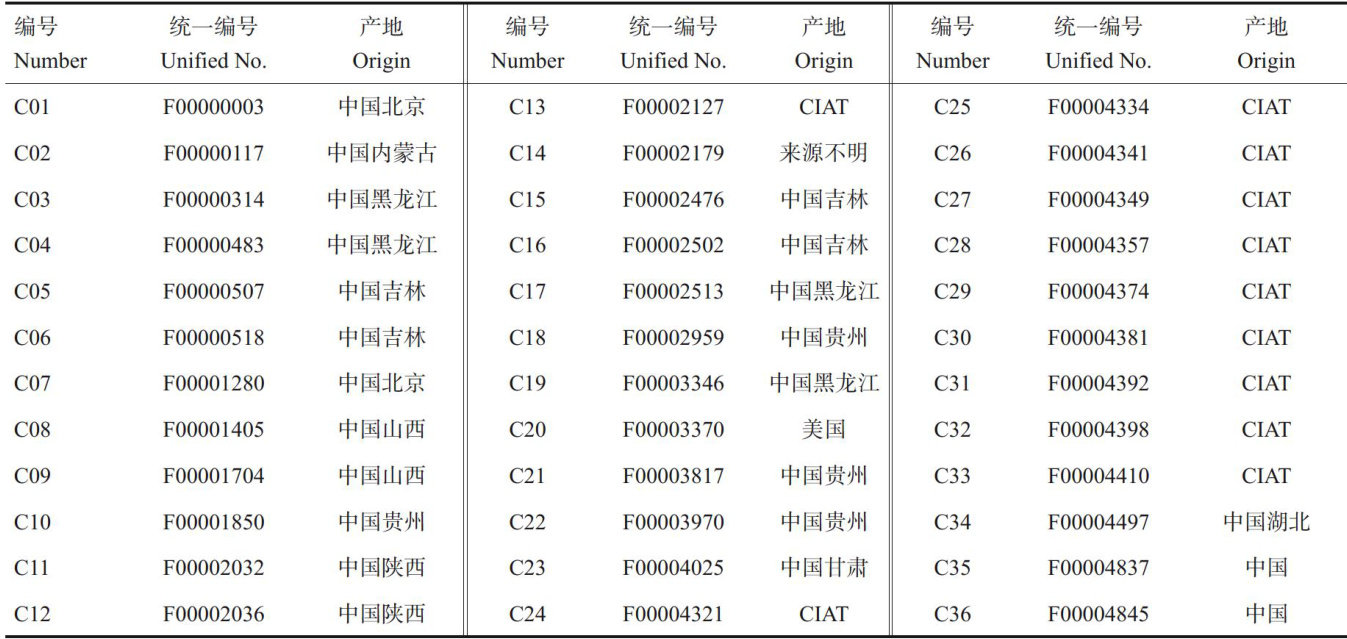
打开文本图片集
Abstract:The common bean (Phaseoluus vulgaris L.) is one of the main edible legumminous crops,drought is one of the most critical abiotic stress constraints limiting common bean growth and productivity. Cultivating drought-tolerant germplasm is an important measure to reduce the adverse effects of drought on the growth of common bean.In this study,6O representative common bean varieties were evaluated through natural drought stress experiments. Comparative physiological analysis between stressed and control groups were performed at 12leaf physiology characters,such as leaf electrical conductivity,water use eficiency and Photosysm II chlorophyllfluorescence parameters. Drought tolerance was assessed by two complementary approaches,visual seedling wilting grade and quantitative drought tolerance subordinate function value ( D value). The results identified seven highly drought-tolerantvarieties(FO000117,F00002179,FO0003370,F00004321, F00000518,F000004381,and Nanyang Black) based on D value. Notably, five of these Varieties (excluding Nanyang Black and FOoo04381)were consistently ranked as most tolerant by applying wilting index. Conversely,six highly susceptible varieties(F00001280,F00003346,F00004357,F00004392,F00005243, and F0005237)showed severe wilting,with five(F00001280,F00003346,FO0004392,F00005243,and F00005237)also exhibiting the lowest D values. The strong concordance between seedling wilting and D (20 assessments validates both methods for drought tolerance screening.The extreme varieties (drought-tolerant vs.
drought-susceptible)identified in this study provide valuable germplasm resources for drought toleranci mechanism analysis and breeding.
Keywords:common bean;seedling;drought tolerance
普通菜豆是世界上主要的食用豆科作物,是人们蛋白质、碳水化合物以及矿物质的主要来源之一。(剩余17675字)