血液代谢物与脑梗死的因果关系:一项两样本双向孟德尔随机化研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R743.33 文献标志码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-1383.2025.07.004
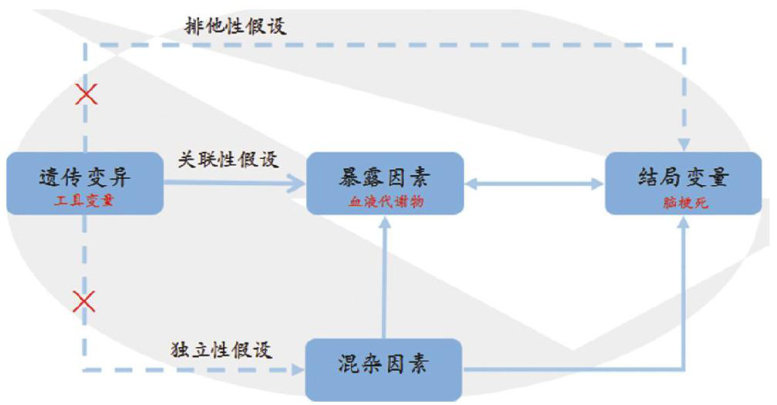
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo explore thecausal relationship between blood metabolitesandcerebral infarction(CI)by two-sample two-way Mendelian randomization(MR)analysis.MethodsThe published genome-wide asociation studies (GWAS)dataof cerebral infarction were obtained from public database.Witha GWAScontaining 140O circulating metabolitesas an exposure indicator,SNPswhich stronglyrelated to exposure factors wereselected as instrumental variables (IV). Thecausalrelationshipbetween140ObloodmetabolitesandcerebralinfarctionwasanalyzedbyR4.3.2software.Fivemethods—MR-Egger regresson,inverse-variance weighted (IVW),weighted median,simple mode,and weighted mode—were employedtoasessheterogeneity,pleiotropy,andsensitivity,therebyverifying therobustnessoftheresults.Finall,a reverse MRanalysis was performedon theobtained results.ResultsIVW method was used to assess causal relationship betweenblood metabolitesand CI,and the results showed that urea (OR=0.997,95%CI: 0.996-0.999)wasa protectivefactor,andtheriskofCIdecreasedwiththeincreaseofmetaboliteurea.ThereverseMRresultsshowedthattherewas nocausalrelationshipbetweenthediseaseandthe metabolites.ConclusionUreahasaninhibitoryefectoncerebral infarction,which may providenewideas and newbasis fortheclinical treatmentand scientificresearchofcerebral infarctionin the future.
【Keywords】metabolites;cerebral infarction(CI);Mendelian randomization(MR);urea
脑梗死(cerebralinfarction,CI)是指一系列脑血管疾病导致脑部供血障碍,局部脑组织缺血、缺氧坏死,进而损害神经功能,甚至发生偏瘫等严重后果的一类临床综合征[。(剩余5500字)