太极拳训练对糖尿病周围神经病变老年人扰动后姿势稳定性的影响

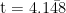
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:804.2 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1009-9840(2025)05-0042-07
Abstract: Objective: To examine the efects of Tai Chi training on postural stability after perturbation in older adults with diabetic peripheral neuropathy(DPN),and to further analyze the relationship between changes in stability and changes in plantar sensation, proprioception, and lower limb muscle strength. Methods :A randomized controlled trial was conducted. Eligible older adults with DPN were stratified by DPN scores and randomly assigned to a Tai Chi group or a control group. The Tai Chi group practiced Tai Chi for 8 weeks, three times per week,60 minutes per session, while the control group received health education. Plantar tactile sensation, proprioception, and muscle strength were assessed before and after intervention. Postural stability was evaluated by calculating the anterior-posterior (AP) and mediolateral (ML) stabilization time after perturbation. Correlation analyses were used to examine the relationships between stabilization time and sensory or motor outcomes. Results: After intervention,stabilization time was significantly reduced in both AP( t= 4.046 , P<0.001 , Cohen's d=0.928 )and ML( , P<0.001 ,Cohen’s d=0.952 ) directions in the Tai Chi group. Improvement in AP stabilization time was weakly correlated with changes in hallux tactile threshold ( r=0.447 , P=0.045 ) and ankle dorsiflexion strength ( r=-0.389 , P= 0.031). Improvement in ML stabilization time was weakly to moderately correlated with changes in ankle plantarflexion strength ( r=-0.558 , P=0.013) ,knee flexion strength ( 0.049),and knee extension strength ( r=-0.394 , P=0.045 ) . Conclusion : Tai Chi training can significantly improve postural stability after perturbation in older adults with DPN. These improvements may be associated with changes in plantar sensation and lower limb muscle strength.
Key words: Tai Chi; diabetic peripheral neuropathy; older adults; perturbation; postural stability
糖尿病(DiabetesMellitus,DM)已成为一个全球性的健康问题,全球约有4.25亿人患有此病,预计到2045年这一数字将上升至6.28亿人[1]。(剩余17219字)