两种喂药方法在新生儿黄疸喂服茵栀黄口服液中效果比较

打开文本图片集
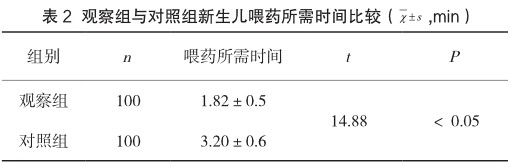
【摘要】目的:两种喂药方法在新生儿黄疸口服茵栀黄中效果进行比较。方法:通过对入住新生儿科的200例需要口服茵栀黄的黄疸患儿进行随机分组,分成两组,对照组(n=100)采用一次性5mL注射器喂药,观察组(n=100)采用一次性奶嘴辅助一次性注射器喂药,对比两组黄疸患儿的反应、喂药时间等方面的差异。结果:观察组黄疸患儿呛咳、呕吐、溢药等发生率明显低于对照组,喂药所需时间较对照组短,差异有统计学意义(P
【关键词】新生儿黄疸;茵栀黄;注射器;奶嘴;口服给药
Comparison of two feeding methods in feeding Yinzhihuang oral liquid for neonatal jaundice
SONG Huifang, LIU Yanlin, DOU Wei, ZHOU Wei Department of Neonatology,Subei People’s Hospital Affiliated to Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, Jiangsu 225001, China
【Abstract】Objective:To compare the effects of two drug feeding methods in oral Yinzhihuang for neonatal jaundice. Methods:200 children with jaundice who needed oral Yinzhihuang were randomly divided into two groups. The control group (n=100) was fed with a disposable 5mL syringe, and the observation group (n=100) was fed with a disposable pacifier assisted with a disposable syringe. The differences in reaction and feeding time between the two groups were compared. Results:The incidence of choking, vomiting and drug overflow in the observation group was significantly lower than that in the control group, and the time of drug feeding was shorter than that in the control group(P
【Key Words】Neonatal jaundice; Yinzhihuang; Syringe; Nipple; Oral administration
新生儿黄疸是由于胆红素(主要是未结合胆红素)在体内积聚引起皮肤黏膜、巩膜的黄染,其发病原因很多,分为生理性和病理性;如治疗不及时,血中未结合胆红素过高,会发生胆红素脑病,导致患儿死亡或严重后遗症,故应加强对新生儿黄疸的临床观察,尽快找出原因,及时治疗[1],护理人员应加强观察和护理。(剩余4530字)