基于景观基因信息链的温州市观音礁村风貌保护与活化策略

打开文本图片集
Landscape Protection and Revitalization Strategies for Guanyinjiao Village in Wenzhou Based on Landscape Gene InformationChain
YUAN Zheng,XU Wenhui*,CHENJiale,JINLinxuan,XULingzi
基金项目:2024年浙江省教育厅一般科研项目“县域传统村落数字化保护路径研究——以诸暨市为例”(编号:Y202455582)
Abstract
Keywords
Island-type traditionalvillages face cultural rupture and landscape fragmentation amid rapid urbanizationand tourism.Using Guanyinjiao Village (Dongtou District,Wenzhou, Zhejiang)asa case,this study,grounded in the'landscape gene information chain' theory,combines literature review and fieldwork,collects 50 semi-structured interviews, and employs NVivo for coding,word-frequency,and co-occurrence analyses.This paperconstructs an indicator system 'occurrence frequency,spatial coverage,cultural importance score,and share of primary functional cognition'to identify thecharacteristics of information elements,information points,and information corridors.Results show that 'fishing-based productionand lifeways'constitute the core information element; traditional stone housesand religious buildings are key carriers of cultural identity,though some exhibit functional alienation; intangible-heritage nodes such as shell carving are declining due to broken transmission chains;and corridor systems prioritize transport over cultural narration.Based onthese findings,this studyproposesa pathway of‘information element restoration-information nodeactivation-information corridoroptimisation,'balancing authenticitypreservationwith revitalisation.
Traditional villages;Landscape genes; Cultural landscape; Activationandutilization;Rural vitalization
文章亮点
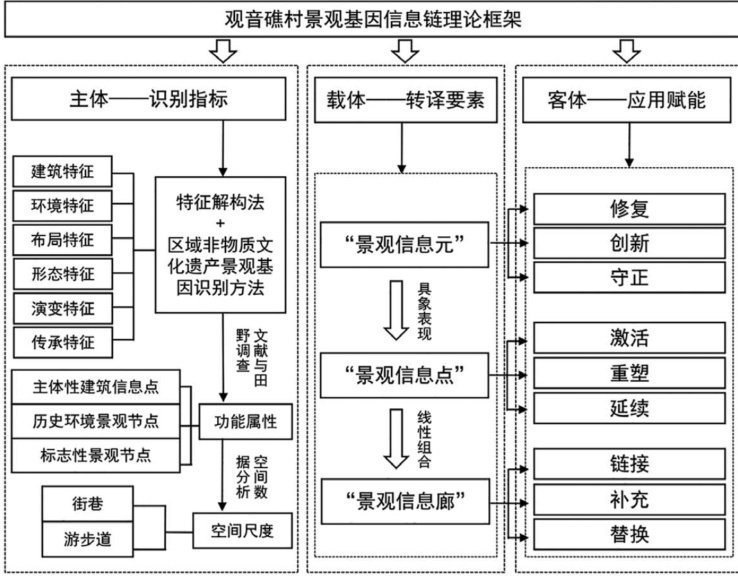
1)基于景观基因信息链理论,构建“识别-转译-应用”流程,基于实地调研与深度访谈,综合利用SPSS、GIS、NVivo等软件,形成可复用的乡村文化景观风貌诊断方法。(剩余9650字)