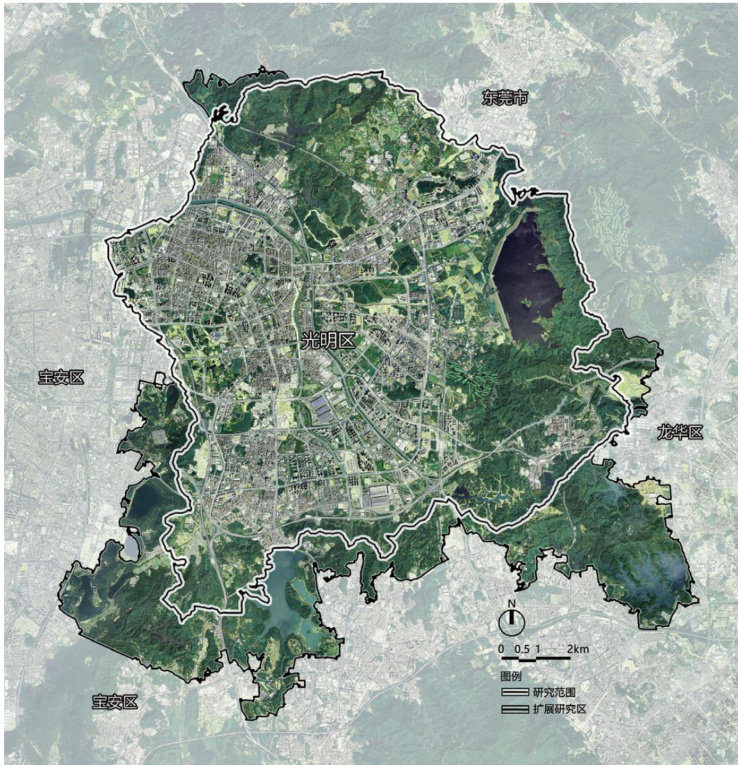
动物生境导向的深圳市光明区景观生态安全格局识别与自然游憩空间优化研究

打开文本图片集
Abstract
Underthe guidance of the goalof modernizing the harmonious coexistence between humansand nature,optimizing nature-based recreational spaces has become an important task in the development of human settlements.Taking Guangming District, Shenzhen asan example,and based on the theory of landscape ecological security patterns,this study employs methods such as morphological spatial pattern analysis (MSPA),graph theory-based connectivityassessment,the minimum cumulative resistance (MCR) model,and circuit theorytoestablishananalytical framework consistingof'habitat matrix identification一high-quality patch selection一corridor network identificationand diagnosis一overall pattern integration'.The results show that the animal habitat-oriented landscape ecological securitypattern in Guangming District comprises three elements:a keyhabitat network consistingof high-core areas (including10 country parksand12urban parks),172 habitat corridorsat three levels,and17 pinch points;6 road barrier points (such as Gongchang Road and Longda Highway);and7types of habitat matrices (core areas,edge areas,etc.).This pattern faces three risks:insufficient synergyamong 'humans, animals,and theenvironment,fragmentationof ecologicalflowsbybarrierpoints,and underutilized functionalpotential of matrixelements.Based on the analysis resultsand practical experience,a three-level optimization strategy is proposed:enhancing network connectivity,restoringbarrierpoints,and improvingbasichabitats.
Keywords
Ecological security pattern; Animal habitat-oriented;Natural recreation space optimization; Morphological spatial pattern analysis; Minimumcumulative resistance model; Graph theory; Circuit theory
文章亮点
1)融合MSPA、图论、MCR与电路理论,构建"生境基底识别-优质斑块筛选-廊道网络识别诊断-总体格局整合”系统性分析框架,显著提升生态源地选择客观性与修复靶向性。(剩余9373字)