氯己定全身擦浴在体外膜肺氧合联合主动脉内球囊反搏泵治疗的心源性休克病人中的应用

打开文本图片集
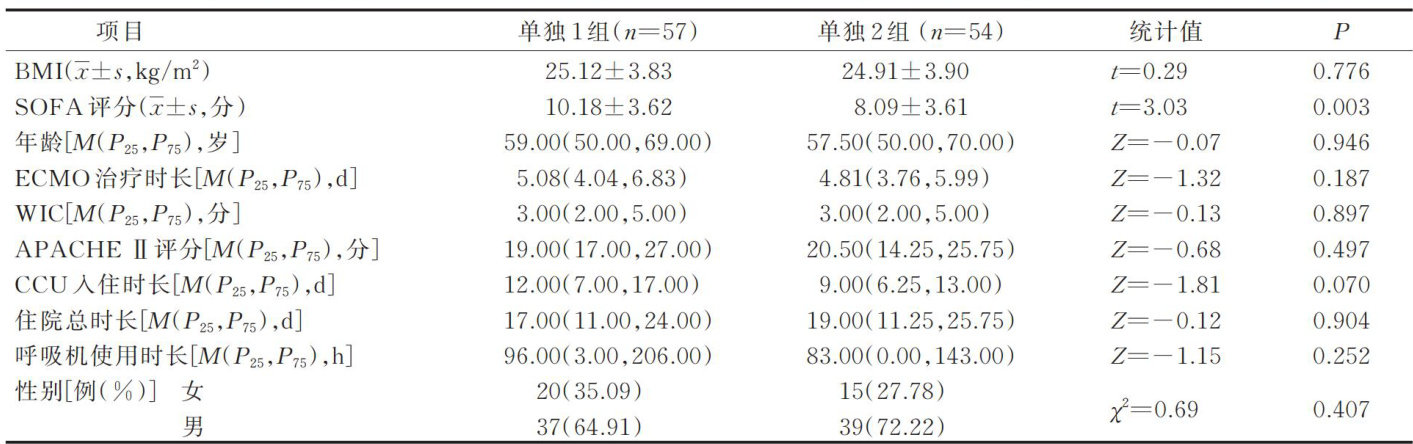
AbstractObectiveToexpletefectofchlorhexidinewolebodyathingfopaientswithcardogenicshocktreatedwiteacopeal membraneoxygenation(ECMO)combinedwithintra-aortic baloonpump(ABP).Methods:Atotalof251patientswithcardiogenicshock admitedtothecardiaccareunit(CCU)ofatertiarygradeAhospitalinHenanProvincespanedformJanuary 2O21toJune2024 wereselectedasthestudysubjectsbycoveniencesaplingTe26patientsadmitedspanedfromJauaryO2ltoDecember222were assignedtotheconventionalgroupAmong tem,57patientswhoreceivedolyECMOtreatmentweredesignatedasseparateintervtion subgroup1.The69 patientswhoreceivedcombined ECMOandIABPtreatment weredesignatedascombinedinterventionsubgroup1. The125patientsadmitedspanedfromJanuaryO23toJune2O24wereasignedtothechlorexidinegroup.Amongthe,54patients whoreceivedonlyECMOtreatmentweredesignatedasseparate nterventionsubgroup2.The71patients whoreceivedcombinedECMO andIABPtreatmentweredesignatedascombinedinterventionsubgroup2.Theconventionalgroupreceived whole-bodybathingwith warmwater,while the chlorhexidine group received whole-body bathingwith 2% chlorhexidine gluconate.The incidence of bloodstream infection(Bingtreantcureompaosfetieaedtalityndthogicroasite patients'blood were analyzed.Results:The BSI incidence in separate intervention subgroup 2 was 11.11% ,and the infection-related mortality was 5.56% .BothofBSIincidenceand infection-related mortality inseparate interventionsubgroup 2werelowerthan thoseinseparate intervention subgroup 1(33.33% and 19.30% ,respectively).The BSI incidence in combined intervention subgroup 2 was 23.94% ,and the infection-related mortalitywas 15.49% .Both BSI incidenceand infection-related mortality in combined intervention subgroup 2 were lower than those in combined intervention subgroup 1(50.72% and 31.88% ,respectively).There were statistically significant differences in terms of the above indicators( P<0.05) 0.Logistic regression analysis showed that whole-body bathing with 2% chlorhexidine gluconate was a protective factor against BSI occurrence.Conclusions: Whole-body bathing with 2% chlorhexidine gluconate could reduce the incidence of BSI and infection related mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock.
KeyWordschlorhexidine; extracorporealmembraneoxygenation;intra-aorticbaloonpump;cardiogenicshock;infection;nursing摘要目的:探讨氯已定擦浴在体外膜肺氧合(ECMO)联合主动脉内球囊反搏泵(IABP)治疗的心源性休克病人中的应用效果。(剩余16220字)