多学科协作的H2H营养管理模式在肝衰竭病人中的应用

打开文本图片集
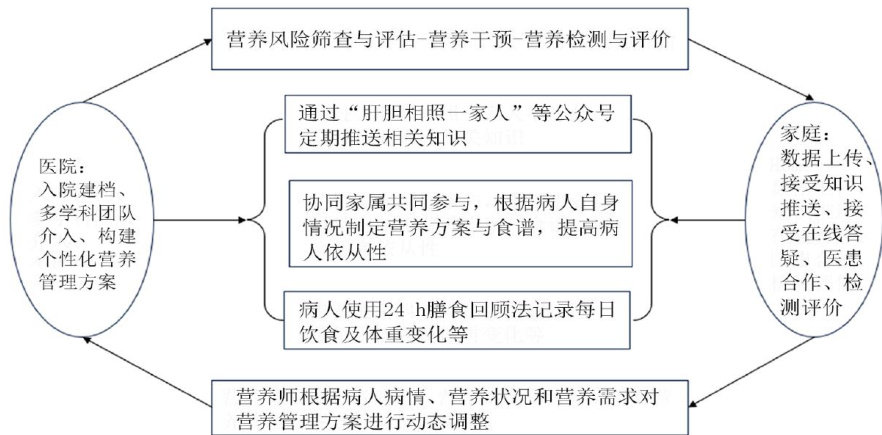
AbstractObjective:ToexploretheefectivenessofmultidisciplinarycollborativeH2Hnutritionmanagementmodelinpatintswith liverlureets:Aotalof9patintsihveflurespidanifectiousdsesdeparmentoffeosseasspial in Wuxicitywereselectedassubjects byconveniencesamplingmethod.Among them,forty-fivepatients admited fromJanuaryto July 2023wereassignedtothecontrolgroup.FortysixpatientsadmitedfromAugust2O23toFebruary2024wereasignedtothestudy group.Thecontolgroupreceivedoutieutritionmaagement.ThestudygroupreceivedtheultidisciplinarycollborativeH2Htrion management modelbasedonthecontrolgroup.Thenutritionalstatus,liverfunctionindicators,ModelforEnd-StageLiverDisease (MELD)score,icidenceofgastrontestialcomplicationsunplanedreadmisionrate,andmortalitywerecomparedbetweehetwo groups.Results:Duringthestudy,patientsinthcontrolgroupand4patientsintestudy groupdroppedout.Finaly42patietsach groupcompletedthestudy.Aftertheintervention,teSubjectiveGlobalAssessment(SGA)gradeinthestudygroupwasbetteranthat in the control group .P<0.05 0.TheRoyal Free Hospital-Nutritional Prioritizing Tool(RFH-NPT) score,albumin(ALB),prealbumin(PA), hemoglobin(HB),bodymassindex(BMI),idar musclecircumference(AMC),andhandgripstrength(HGS)weresupeririestudy group than those in the control group P<0.05) .Incontrast,alanine aminotransferase(ALT),aspartate aminotransferase(AST),total bilirubin (TBiL),protho),Eototaleofrteilpasndpdadisieelor in the study group than those in the control group ΔP<0.05 ).Conclusions:The multidisciplinary collaborative H2H nutrition management modelcouldimproveteutrioasatusandliverfuoofpatientwithliverfle.Itasoouldedueteicideeofsttetial complications and unplanned readmission rates of patients.
Keywordsuiiialbotioraagnt;lefeoalasuios摘要目的:探讨多学科协作的H2H营养管理模式在肝衰竭病人中的应用效果。(剩余10329字)