人工智能化、人力资本水平对碳排放绩效的影响
——基于长江经济带数据的实证分析

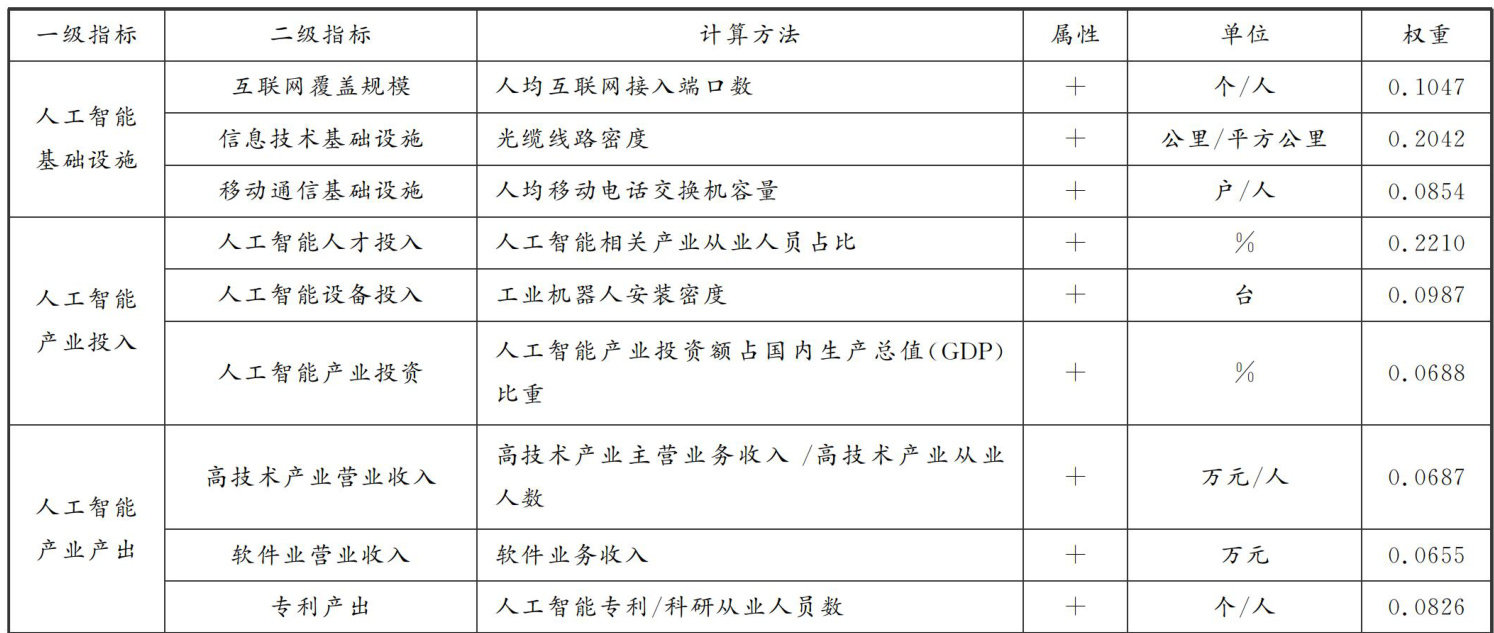
打开文本图片集
【中图分类号】F127 【文献标识码】A 【文章编号】2095-7009(2025)04-0075-10
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Human Capital on Carbon Emissions :
Empirical Evidence from Yangtze River Economic Belt
DING Min',ZHAO Yu2 ,WAN Zi-xin³
(1. Department of Economics and Management, Bozhou University, Bozhou 2368Oo,Anhui, China ;2. School of Chinese National Community, South-Central Minzu University, Wuhan 430074,China ;3. School of Economics and Management , Yangtze University, Jingzhou 4340o, Hubei, China)
Abstract:Based onpaneldata from theYangtze River Economic Beltspanning 2011 to 2O23,this studyempirically examines the impact andunderlying mechanisms ofartificial intellgencedevelopment and human capitallevelsoncarbonemission performance using fixed efects and moderation effect models.The results show that both the advancementof artificialintelligenceand improvements inhumancapitalsignificantlysuppresscarbonemisions.Regionalheterogeneityanaly sis reveals thatthecarbon-reducing efectofartificialintellgenceis mostpronounced inupstreamregions,followed by downstreamand then midstream regions.In contrast,the suppressive efect of human capital on carbon emissions is strongest in downstream areas,folowed byupstream and finally midstream regions.Mechanism testing further ndicates thathigherlevelsof humancapitaltend to weakentheemission-reducing effectof artificial intelligence.Therefore,itis recommended todeepentheintegrationofartificialintellgence intheupgradingof traditional industries,acceleratethe green digital transformation,optimize regionalhuman capital allcation,strengthen talent support for gree industries, and promotecolaborative innovationbetweenartificial intellgence and high-end talenttoestablishregional models for low-carbon development.
Key words:artificial intelligence;humancapital;carbon emisionperformance;fixed effects model;moderation efect model
一、引言
党的二十届三中全会明确提出,“中国式现代化是人与自然和谐共生的现代化”,强调要“聚焦建设美丽中国”,加快经济社会发展全面绿色转型[]。(剩余12209字)