98份燕麦品种(系)茎秆抗倒伏性状的综合评价
打开文本图片集
doi:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2025.08.017
中图分类号:S543.7 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1007-0435(2025)08-2567-08
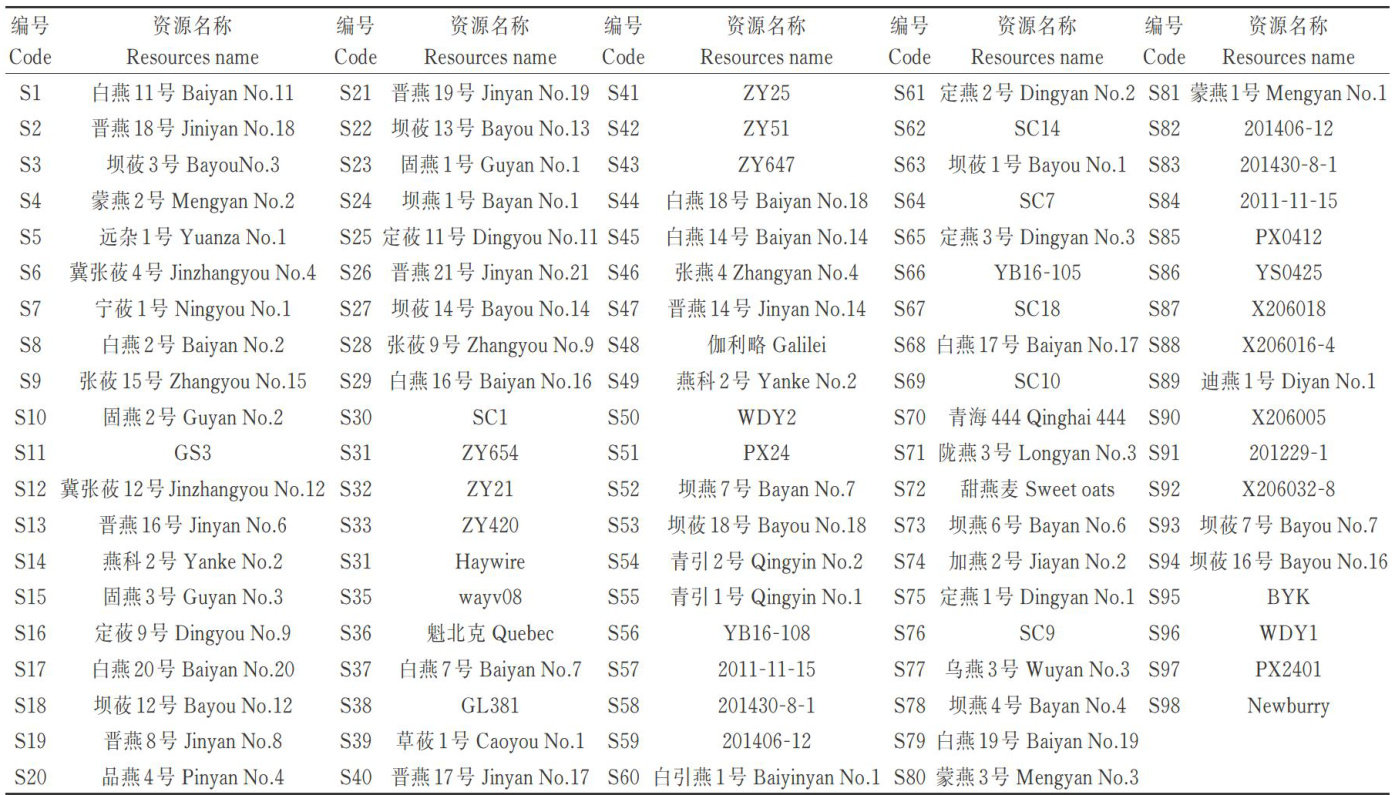
Abstract:Inordertounderstandthelodging resistancecharacteristics ofoatstems,descriptiveanalysis,correla tion analysis,cluster analysis and principal component analysis were conducted on l3 traits of 98 domestic and foreign oat varieties(lines)in this experiment.The results showed that 98 oat varieties(lines)had significant differences in diferent traitsand relatively rich variations.Among them,thecoeficients of variationof three traits,namely the length of the second internodeat the base of the stem,the flexural resistance of the second internode at the base of the stem,and the thickness of the stem wall,were all greater than 40% .Regression analysis revealed that stem thickness and stem wall thickness were the core indicators for evaluating lodging resistance,with a comprehensive contribution of 29% .Based on the cluster analysis of 13 stem characteristic indicators,98 oat varieties(lines)could be divided into 3 groups.Among them,the first and third groups were the anti-lodging group,and the second group was the easy-to-lodging group. Through field observation and comprehensive evaluation of principal components,materials such as ZY25,XZ06oO5,Bayou No.13,Yuanza Nol,WDY1,PX0412,X2060388 and Baiyan No.2O were screened out as excellent anti-lodging germplasms. It is preferred in anti-lodging breeding.
Key words:Oat;Stem characteristics;Lodging;Comprehensive evaluation
燕麦(AvenasatiuaL.),作为一种营养丰富、适应性强、抗旱耐寒的重要粮食作物和饲草料作物,在全球范围内,特别是在北半球的温带地区广泛种植,其一般分为带稃型和裸粒型两大类,前者称为皮燕麦或普通燕麦(A.satiaL.),后者称为裸燕麦(A.nudaL.)[1]。(剩余10506字)