感离蠕孢叶斑病多花黑麦草叶际微生物群落结构与多样性分析
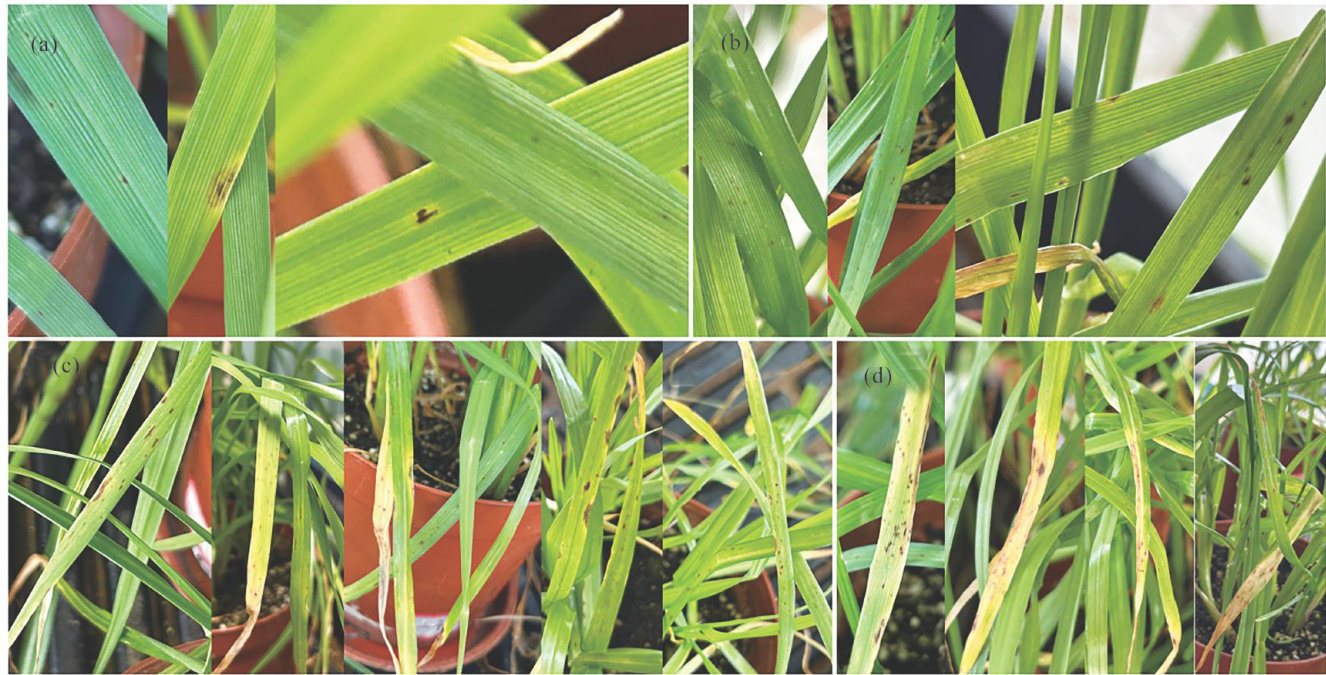

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S435.4 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1007-0435(2025)08-2423-1
Abstract:To investigate the changes of the structure and diversity of the phyllosphere microbial community after infection of Italian ryegrass(Lolium multiflorum) with Bipolaris sorokiniana,this study was conducted by artificially inoculating Italian ryegrass with B . sorokiniana spore suspension and collecting leaves of infected and healthy Italian ryegrass. High-throughput sequencing was used to investigate diferences in the structure and diversity of the phyllosphere microbial community.Results showed that there were significant differences in phyllosphere microbial community structure,and the species richness and diversity of phyllsphere fungi and phyllosphere bacteria were higher in infected leaves than in healthy leaves.The dominant bacterial phylum was Proteobacteria and the dominant fungal phylum was Ascomycota.Functional prediction revealed a significant increase in potential pathogenic phenotypes following the infection of Italian ryegrass,with the Proteobacteria contributing substantially to the pathogenic phenotypes.Differences in abundance of Proteobacteria across groups were consistent with trends in pathogenicity phenotypes.This study provides a theoretical basis for the mechanism of plant phyllosphere microbial community responses to pathogen infection.
Key words:Lolium multiflorum; Bipolaris sorokiniana; Phylosphere microbial community;Diversity;Highthroughput Sequencing
多花黑麦草(Loliummultiflorum)是一种高产优质牧草和草坪草,在世界各地广泛种植,具有较高的环保价值和经济价值,随着我国西南地区黑麦草的广泛种植,其病害的发生对多花黑麦草的生产和利用造成较大经济损失[1-3]。(剩余16163字)