不同放牧强度对荒漠草原土壤活性有机碳的影响
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S812.2 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1007-0435(2025)08-2541-07
doi:10.11733/j.issn.1007-0435.2025.08.014
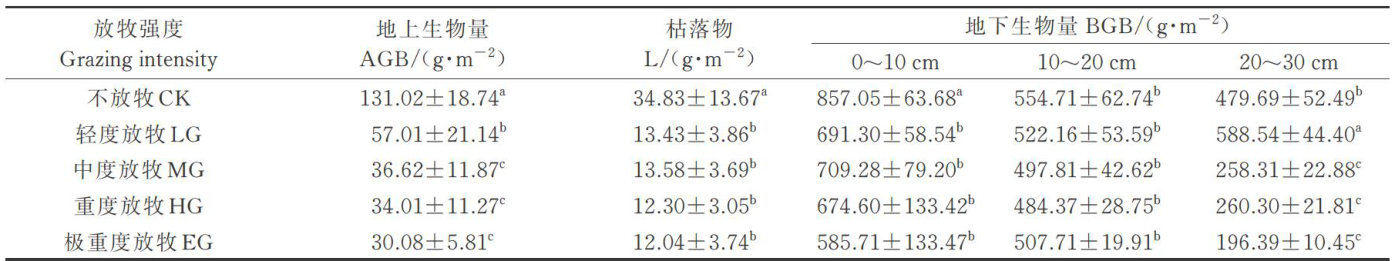
Abstract:The effects of different grazing intensities on soil active organic carbon in desert steppe were studied to understand the regulation mechanism of grazing on soil organic carbon,aiming to provide a theoretical basis for reasonable control of grazing intensity. In this study,desert steppe with Stipa breviflora as a dominant spe cies in Inner Mongolia was used as the research object to determine the content of soil organic carbon and its active components,soil physical and chemical properties,abovegroundand belowground biomass and liter amount. The results showed that the soil organic carbon (SOC) content in the non-grazing treatment was significantly higher than that in the grazing treatment ( P<0.05 .With the increase of grazing intensity,the soil total nitrogen(TN) content decreased gradually,and the soil alkaline nitrogen(AN) in non-grazing treatment was significantly higher than that in grazing treatment ( P<0.05 .The soil bulk density(BD)and pH value increased gradually,and the non-grazing treatment was significantly lower than that in grazing treatment ( ⋅P< O.05).Aboveground biomass(AGB),belowground biomass(BGB)and liter(L)decreased with the increase of grazing intensity. The corelation analysis of SOC and its components and physical and chemical properties showed that SOC content was significantly positively correlated with soil TN,AN,aboveground biomass (AGB) and content,and SOC content was significantly negatively correlated with soil BD and pH. The results of this study showed that overgrazing significantly reduced soil organic carbon.Therefore,it is recommended to maintain grazing intensity at light grazing(1.54 sheep‘ hm-2⋅a-1) can effectively maintain grassland productivity and protect soil organic carbon.
Key words:Grazing intensity;Desert steppe;Soil organic carbon;Biomass
在陆地生态系统的构成中,草地生态系统占据了至关重要的位置,它覆盖了大约5000万 km2 的土地,并且拥有 28%~39% 的陆地土壤碳储备,具有极大的碳汇潜力[1-2],因此,即使草地生态系统土壤有机碳(Soilorganiccarbon,SOC)含量的微小变化也可能影响全球碳循环[3]。(剩余11789字)