淤泥固化土的静力特性研究
打开文本图片集
DOI:10.19860/j.cnki.issn1005-8249.2025.04.014
KONG Lingyi,QI Xionggui², ZHU Fuqiang',LI Yinlu²,MENG Lijun², ZHU Yongyang³ (1. China Construction Port Construction Group Co., Ltd., Qingdao 266O11,China; 2.Tai'an City Transport Bureau Port Aviation Railway Airport Service Center,Tai'an 271OO,China; 3. Geotechnical Research Institute of Hohai University,Nanjing 21Oo98,China)
Abstract:Thisstudyinvestigatedtheefectsofinitial watercontent,cementdosage,flyash content,andcuringageonthe staticcharacteristicsof sltsolidifiedsoil throughunconfiedcompresivestrengthtests.Theresultsindicatedthatthestrengthof thesolidified soildecreasedwith increasing initial watercontent.Theminimumcement dosagesrequiredto meetthestrength criterion for railway subgrade surface layers ( 500kPa )were 6% , 8% ,and 10% at initial water contents of 50% , 60% ,and 70% ,respectively.Alinear relationship wasobserved between cement dosage and strength,with extrapolated zero-strength cement thresholds of 1.28% , 2.24% ,and 3.31% for the three water content levels. The influence of fly ash on strength exhibited water content dependency : strength decreased with fly ash addition at 50% water content,showed an initial increase followed by reduction at 60% water content,and demonstrated progressive enhancement at 70% water content. The strength increased throughout the 28- day curing period,with higher growth rates observed during the 7-14 days phase compared to the 14-28days phase.Thesefindings elucidatethecoupled efects of multiple factorsonstrength evolutionand provide practical mixproportion guidelines for the resource utilization of dredged silt. Key words: silt solidified soil;cement;fly ash; static characteristics;peak strength
0 引言
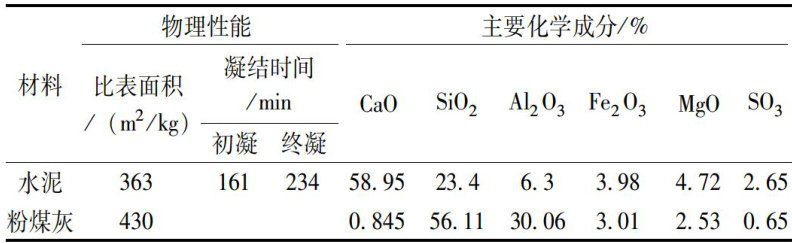
疏浚淤泥的规模化弃置引发土地占用与二次污染风险,其资源化利用亟需解决力学性能不足的核心瓶颈。(剩余7402字)