百山祖国家公园生态系统服务权衡与协同效应及其驱动因素分析

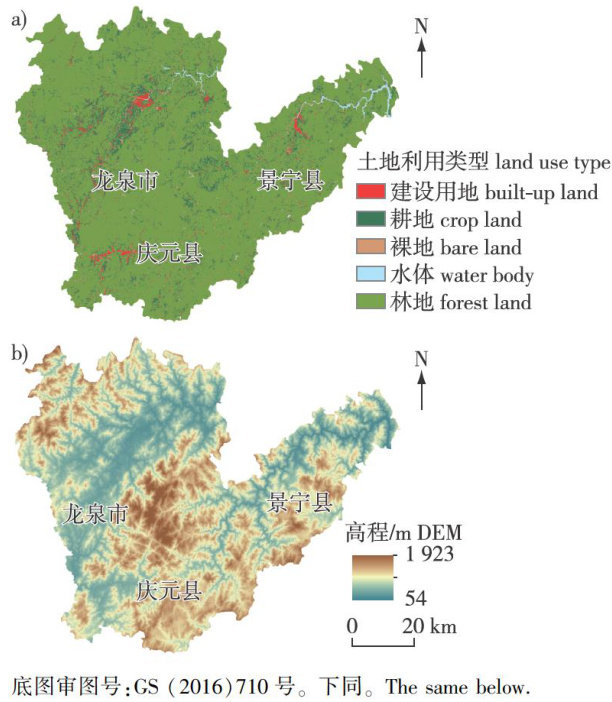
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S718;Q148 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-2006(2025)05-0249-09
Abstract:【Objective】This study explores the trade-ofs,synergies,anddriving factors among the ecosystem services in Baishanzu National Park,providing support for formulating scientific ecological protection and management strategies. 【Method】We quantified four ecosystem services-vegetationnet primary productivity(NPP),soil conservation(SC), habitat quality(HQ),and water yield(WY)-in Baishanzu NationalPark from20OO to2O2O byusing the InVESTand the CASA models.Spearman corelationand geographically weighted regression(GWR)were used toanalyze the relationshipsof trade-ofsand synergies among ecosystem services,while therandom forest modeling was used to explore the dominant driversandmarginal efects.【Result】From2OOO to2O2O,theNPPinBaishanzu NationalPark nature reserve increased,theHQdeclined slightly,andtheSCandtheWYdecreased initiallbeforerising.Spatially,the NPP,the SC,and the WY exhibited similar paterns with high values in central/northwestern regions,whereas the HQ peaked i central/northernareas.The increase in temperaturehadasignificant impacton therelationship between the HQand theNPP,while precipitation,elevation,andslope hadasignificant impactonthe relationship between the SC and theWY.【Conclusion】The four ecosystem servics demonstrated anoverall synergy but showed obvious spatial heterogeneity.Climate changewastheprimarydriverof trade-ofs/synergies,followedbythe degreeofvegetation coverageandterrainfactors.Thisindicatesthatwhenformulating ecological strategiesmust thereforeaccount for interactions among these key factors and their potential nonlinear effects.
Keywords:ecosystem services;trade-offand synergy;spatiotemporal variation;geographically weighted regression; randomforest;BaishanzuNational Park
生态系统服务是指自然界向人类直接或间接提供的各种利益[1],森林生态系统为人类提供了各种各样的服务,包括土壤保护、气候调节和生物多样性维持等,同时也为人类提供了经济、社会和文化价值[2-3]。(剩余14784字)