麋鹿野放对盐城滨海湿地土壤生态化学计量特征的影响

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S713;S154.1 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-2006(2025)05-0038-07
Abstract:【Objective】ThisstudyaimedtoinvestigatetheimpactsofElaphurusdavidianusdisturbanceonsoilecological stoichiometry inYancheng coastal wetlands,assess the current stateof soil degradation,andprovideascientific foundation for thesustainablemanagementofthereserve.【Method】ThethirdcoreareaofYancheng Dafeng Milu National NatureReserve wasselectedas thestudysite.Basedon field surveys,theareawas stratified into fivedisturbance intensity levels:weak(I),mild(II),moderate(II),secondaryheavy(IV),and severe(V).Soil physicochemical properties, including bulk density(BD),soil water content (WC), pH ,the content of soil organic carbon(SOC),total nitrogen(TN),and total phosphorus(TP),were measured through laboratoryanalyses.The efectsofvarying disturbanceintensitiesonsoil propertiesand ecological stoichiometricratiosweresystematically evaluated.【Result】(1)With the increase of E ,davidianus disturbance intensity,soil BD frist decreased,and then increased,soil pH increased,while soil TN,TP contentand soil WC first increasedand then decreased,and SOC content showed a fluctuating trend.(2)With the increase of E .davidianusdisturbance intensity,the soil C/N(mass ratio)increased,thesoilN/P(massratio)decreased,andthesoilC/P(massratio)fluctuated.(3)Thecorelations between soil C/Pand SOC,and between soil N/PandTNwere extremelyhigh,and the correlation between C/Nand SOC gradually decreased with the increase of E . davidianus disturbance intensity. SOC content was the main limiting factor of soil C/N and C/P ,and soil TN content was the main limiting factor of soil N/P.【Conclusion】 E . davidianus disturbancenotonlychanges thebasicsoil propertiesandecological stoichiometriccharacteristics,but alsochanges the intensity of soil stoichiometric ratios.Moderate and mild disturbance of E .davidianus is more conducive to soil mineralization and nutrient cycling.These findings suggest that maintaining E .davidianuspopulationswithin areasonable threshold is critical for preserving soil nutrient equilibrium in Yancheng coastal wetlands.
Keywords:Yancheng coastal wetlands;Elaphurusdavidianus (elk); soil basicproperties; ecological stoichiometriccharacteristics
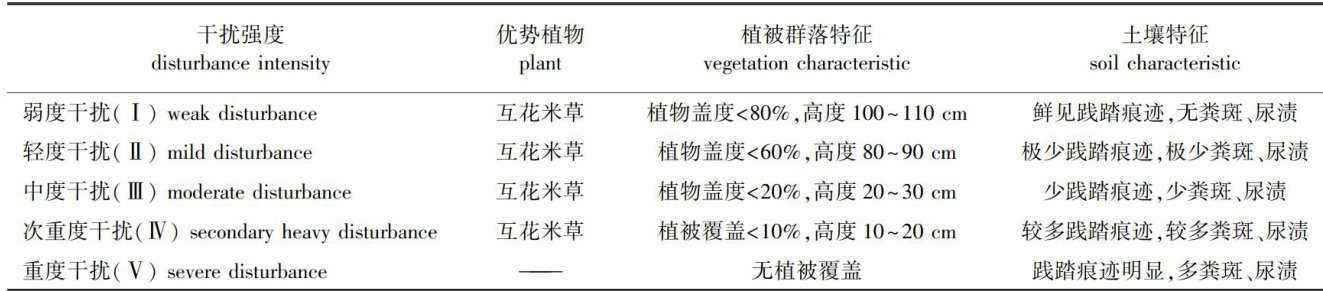
土壤生态化学计量特征主要反映土壤碳(C)、氮(N)、磷(P)之间的平衡关系[1-4],可为土壤退化评价提供科学依据。(剩余15737字)