天然饲料与人工饲料对小菜蛾幼虫发育和生理生化的影响

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S852.4 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1671-4652(2025)05-0128-07
ABSTRACT:The diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella)is a major agricultural pest. Studying the efects of natural and artificial diets on the growth,development,and physiological biochemistry of P .xylostella larvae aims to optimize artificial diet formulationsand provide higher-qualitytestinsects forscientific research.Theresults showedthat,compared to larvae fed with a conventional artificial diet,those fed with a natural diet exhibited that over 50% higher total sugar and total protein content and a 14.3% decrease in fresh weight. After adjusting the glycogen ratio in the conventional artificial diet,significant changes were observed in larvaltotal sugar and protein content. Increasing glycogen proportion significantly raised totalsugar levels,and decreasing glycogen proportion significantly reduced both total sugar and protein content.Additionally,the groups fed with a higher propertionof glycogen-sugar diet showed significantlylower survival and pupationratescompared tothe control group.The groupsfed with alower propertionof glycogen-sugar diet exhibited significantly higher adult emergencerates.Inconclusion,diferenttypesof diets significantlyafectthe development and physiological biochemistry of P . xylostella larvae. Adjusting the glycogen ratio can influence larval phenotypic plasticity, thereby providing test insects of varying quality to meet the demands of scientific research and other applications.
KEYWORDs:Plutellaxylstell;naturaldiet;artficialdiet;glycogenratio;growthanddevelopment;physlogicalchstry
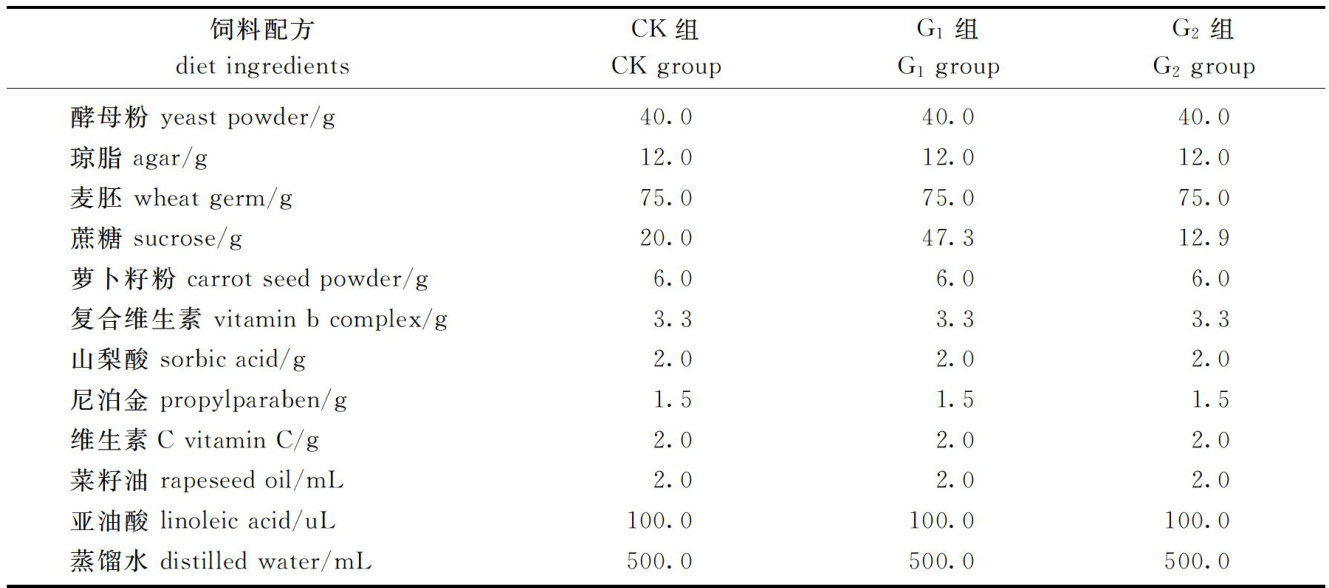
小菜蛾(Plutellaxylostella)属鳞翅目菜蛾科,又称吊丝虫,主要危害十字花科蔬菜,是一种重要的农业害虫。(剩余10274字)