液基细胞学检测中人工智能及人工诊断的对比研究

打开文本图片集
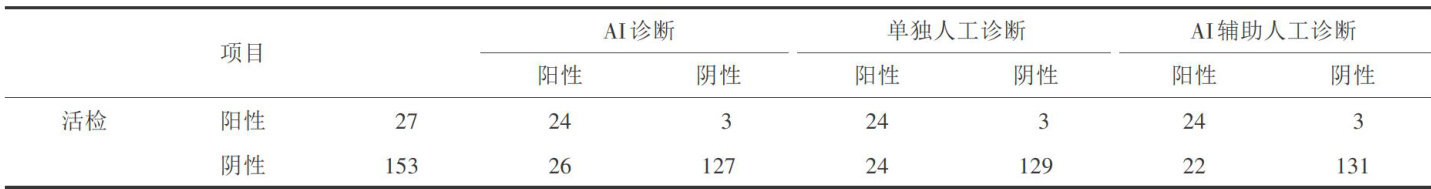
【Abstract】 ObjectiveTo explore the consistency of artificial intellgence (AI)-assisted diagnosis and artificial diagnosis in liquid-based cytologydetection and screening.MethodsOne hundredand eighty patients who underwent LiquidBased CytologyTest (LCT)at Zhongshan People's Hospital were colected.Thepathological results ofcervical biopsy tissue were used asthe judgment criteria to analyze and comparethe AI diagnosis in LCT withindividual manual diagnosisandAI asisted manual diagnosis,as well as diferent pathological subtypes, sensitivity,specificity,and ROC curve area comparison.ResultsPathological cervical biopsy,as a diagnostic criterion,showedstatisticallysignificantdiferencesbetweenAIdiagnosis,standalonemanualdiagnosis,andAI assisted manual diagnosis ( χ2 =82.588,87.353,92.532,P<0.01).The accuracy,specificity,and sensitivity ofAI diagnosis were 83.89% , 83.01% ,and 88.89% ,respectively,with similar results in differentpathological subtypes; The accuracy,specificity,and sensitivity of individual manual diagnosis were 85.00% , 84.31% ,and 88.89% respectively.The accuracy of AI assisted manual diagnosis is 86.11% ,the specificityis 85.62% ,andthe sensitivity is 88.89% .And thelower productof theROCcurveforAI asisted manual diagnosis isslightlyhigher than that for AI diagnosisand manual diagnosis alone.ConclusionCompared with liquid based cytology screening,AI asisted manual diagnosis exhibits slightly better accuracy,specificity,and sensitivity.
【Key words】Artificial intelligence;Pathological diagnosis;Liquid-based cytology detection;Cervical cancer screening DOI:10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2025.07.012
宫颈癌在女性生殖系统肿瘤中的发病率和死亡率均占显著地位,是全球女性最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。(剩余6287字)