不同茶树品种茶橙癭螨种群动态及其与环境因子的关联性研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S571.1;S431.3文献标识码:A
文章编号:1000-3150(2025)08-57-5
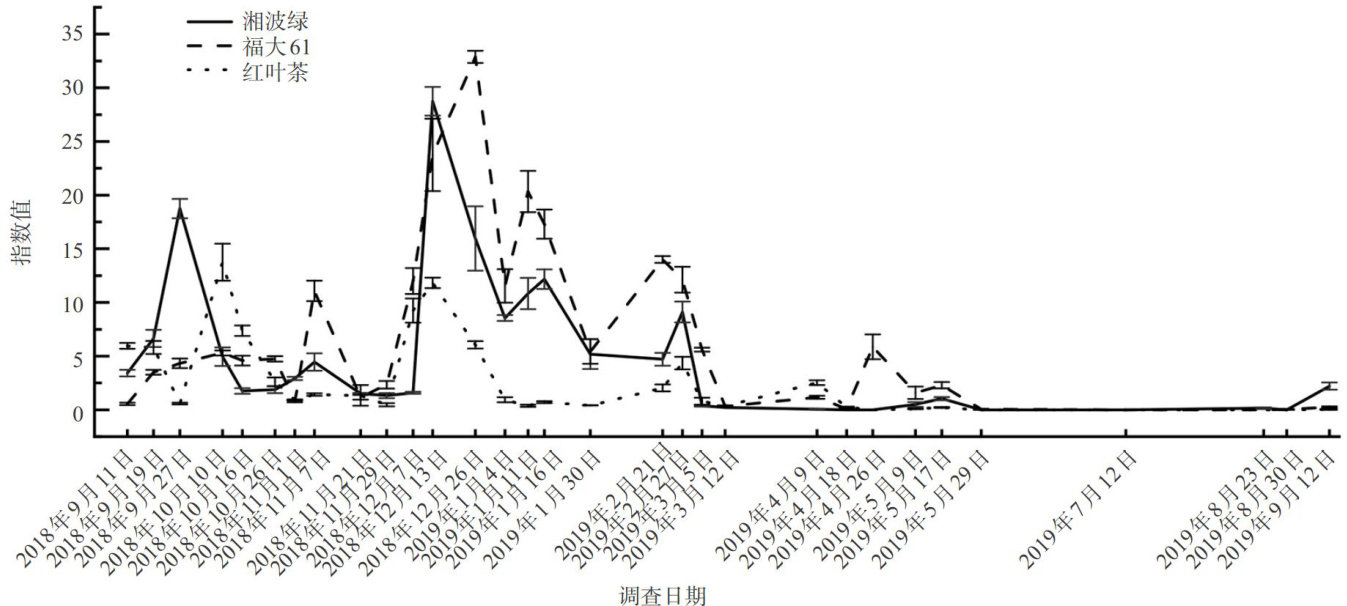
Abstract:To investigate the populationdynamics andenvironmental drivers ofAcaphylathee,this studyconducted a one-year field monitoring of three tea cultivars:'Xiangbolu',Fuda61',and'Hongyecha'.The mite populations at difrent leaf positions and their relationship with temperature were systematically analyzed.The resultsshow significant variations in miteresistance among thecultivars.Fuda 61'hadthe highestannual miteoccurrence,withanaverageannual index of6.61,which was 1.37 times thatof'Xiangbolu'and2.55 times thatof'Hongyecha'.Mites were primarily concentratedon the third leaf below the budfor'Xiangbolu'and'Hongyecha',andonthe fifth leaffor'Fuda 61'. Temperature regulation exhibitesa dual-threshold effect: low temperatures in winter ( ≤10∘C )facilitated population outbreaks, with the index reaching up to 21.90, while high temperatures in summer ≥25∘C )significantly suppressed mite activity.This studyelucidates theoccurrence paternsofAcaphylla theaeand itsrelationships with teacultivars, leaf position distribution,and temperature,providing ascientific foundationforprecisemitecontrol,tea gardencultivar optimization, and the development of climate-responsive ecological management strategies. Keywords: Acaphylla theae, tea cultivars,seasonal fluctuation,leaf position distribution, temperature
茶橙癭螨(AcaphyllatheaeWatt)又名斯氏尖叶癭螨,属蜱螨目癭螨科,是茶树主要害螨之一。(剩余5056字)