纳入慢病管理的2型糖尿病患者用药依从性及相关影响因素分析

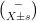
打开文本图片集
关键词:2型糖尿病;用药类型;家庭医生服务;慢病管理;用药依从性;COX回归模型中图分类号:R587.1 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2025.14.009
文章编号:1006-1959(2025)14-0057-05
Abstract:ObjeeToivestigatepaedifuenngfctooftyabeselltspatitsderocdiseasaat andtoprovideeferefgocsaseaagntetsI16pisieeeslisoid upforchronicdiseasemanagementservicesfroaealthservicecenterinTicangCityererandmlyseleteepatientsmedicationcoplance wasinvestigatedbyMMAS-8questioaireandbsicdatacoletionandtheelatedinflueningfactorsereanalyedbyCOXisodel. ResultsTheaveragsof8inpatintsitdabeteelitusudedioiciseasemaagmes)soe medication compliance was poor in 29 cases (8.03 % ),general in115cases (31.86 % ),and excellent in 217 cases (60.11 % ).The survey results showed thatthethreeainomplanceenomnaereotaingediciotie,ometisforgetingtotakeedicinendself-esingor decreasingorstoppingmedicationduring treatment.MultivariateCOXregresionanalysisshowedthat thecourseofdisease( B= -0.048,P=0.025),the number of hypoglycemic drugs(B=-O.680,P=O.016),and the level of education( B= -0.940,-0.676,P=O.0O1) were negatively correlated with poor medication compliance;the level of fasting blood glucose( B =0.111, P =0.040) was positively correlated with poor medication compliance;the probablityofredicatiooplinceiosmoksasghetanthatikers(B6,O8).Ccusinedicai compliancfloatilitisieldi disease,theumbrofglcdugndelevefucaindosiivlyelaedioistigbloduoleels Continuousatention should be paid to patients'medication compliance in chronic disease management.
KeyWords:TebeesdicatiotFmilyoctorseice;Cociesemaagentedicatiolce;COeel
糖尿病(diabetes)是常见的慢性病之一,目前我国糖尿病患病人数居世界首位。(剩余6601字)