茶树CsTLRs基因密码子偏好性与进化分析

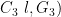
打开文本图片集
Abstract:The TLR gene has thefunction ofregulating the growthand development of planttrichomes.Leaftrichome is oneof theimportantmorphological characteristicsofCameliasinensis(L.),which playsanimportantroleinthephysiology and ecology of tea plant and tea quality.In this study,we conducted a comprehensive analysis of tea plant CsTLRs genes, including codonparameters,geneticrelationshipand heterologous expresion hosts.This wasachieved using multipleanalytical approaches including neutral plot analysis,parityrule2 plot(PR2-plot)analysis,implemented through softwares such as CodonW and EMBOSS.The results showedthatthe codon usage bias of CsTLRs genes was weak,and the bias was primarily dominated by natural selection. There were 2O optimal codons in CsTLRs genes,mostly ending with A/U . Both cluster analyses of the coding sequences (CDS) and relative synonymous codon usage ( RSO )revealed that CsTLRs genes in tea plant
werephylogenetically closer to those in poplar(Populus) andcucumber(Cucumissativus). Forheterologous expression of CsTLRs genes from tea plant,tobacco (Nicotianatabacum),Arabidopsis(Arabidopsisthaliana),and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) could be selected as genetic transformationrecipients,while the expression inmicroorganisms was better in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.In summary,this study analyzed the codon usage biasof CsTLRs genesintea plants,elucidating theircharacteristic codon
usagepaterns during theregulationofleaftrichomedevelopment.Thesefindings would providereferencesforfuturefunctional studies of CsTLRs genes.
Key words: tea plant;leaf trichomes;CsTLRs genes;codon bias;evolutionary analysi:
密码子由mRNA上编码氨基酸的3个核苷酸序列组成。(剩余17970字)