天津滨海中心区绿地重金属含量特征及风险评价研究

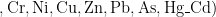
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X820.4
文章编号:1674-6139(2025)07-0178-05
文献标志码:B
Characteristics and Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metal Content in Greenland of Tianjin Binhai Center Area
Li Shuo’,Hou Jiantao²,Gao Hongsheng',Wu Jin²,Ma Wuming (1.Tianjin Institute of Geological Survey,Tianjin 300191,China; 2.Tianjin Monitoring Central Station of Geological Environment,Tianjin 3Oo191,China)
Abstract:Inodertovestigatethedistributionpolltionessment,andpotentalecolgicalissofametalsineee spacesoftheBnhaiCentralDistrict,17soilsamplesfromteseareaswereanalyed.Theconcentrationsofeightheavymetals(Cr,Ni, Cu,Zn,Pb,AsHg,d)ndpeesereesudUsingomprativenalysis,eosatisticalalysis,ltionldided theimprovedHankansonecologicalriskindex,thestudyrevealedthefolowingresults:Althoughtheheavymetalconcentrationsinthe green space soils did not exceed the Level II screening values,there was a certain degree of accumulation.The concentration of Cr,Ni, Cu,Zn, Pb ,andCdwashighestinthesoutheast,folowedbythecentralregion,andthenthenorthwest.Hgconcentrationwas highest inthecentralgiongreaterthanthatintesoutheastandorthwestareas.HighconcentratiosfAsweredistrbutedtrouhotee gion,withthepriaryaluelcatedinesotheastetetialcoloicalisksssetidicatedattedyeais at moderate ecological risk,with Hg and Cd being the main contributing factors.Points of strong and very strong ecological risk are mainlylocated in thesoutheastern part of the studyarea,near the transportation routes leading to TianjinPort.
Keywords:green space;heavy metal;environmental assessment;ecological risk
前言
城市绿地是城市生态系统的重要组成部分,具有重要的生态、经济、社会和景观效益[1]。(剩余4956字)