基于代谢组学探讨消食白头翁汤治疗溃疡性结肠炎的疗效及机制

打开文本图片集
关键词:消食白头翁汤;溃疡性结肠炎;代谢组学;苷类代谢;嘧啶代谢;小鼠中图分类号:R285.5 文献标志码:A文章编号:1003-9783(2025)07-1123-08doi:10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2025.07.010
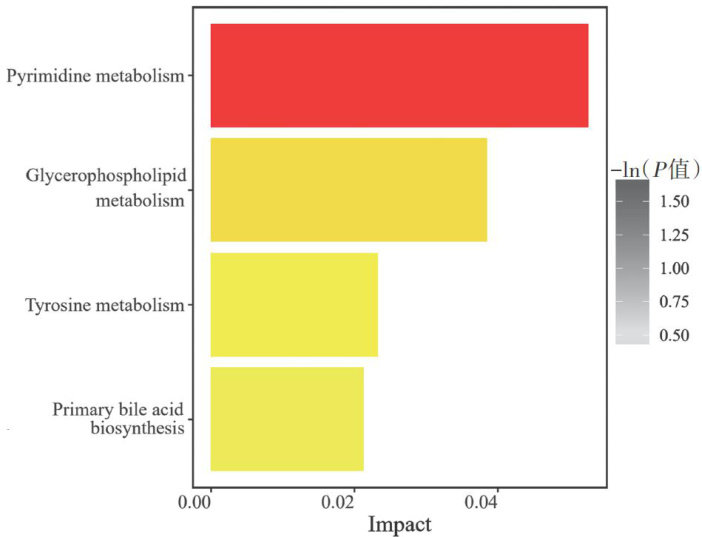
Abstract:Objective To investigate the therapeutic efects andunderlying mechanisms of Xiaoshi Baitouweng Decoction(XBD)inulcerativecolitis(UC) mice.Methods Mice were randomized into normal,model,Mesalazine, XBD low-dose,and XBD high-dose groups using a random number table.A UC mouse model with "damp-heat syndrome of the large intestine" was established via a "high-fat high-sugar diet + alcohol + artificial climate incubator" protocol combined with 3% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS). Corresponding treatments or pure water were administered via gavage over a 22-day modeling period.Disease activity index (DAI)and histopathological scores were calculated, colon length was measured,and colon morphology was assessed via hematoxylin-eosin(HE) staining.ELISA was used to detect IL- 1β and TNF- α levels in colon tissues,while ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with Fourier transform mass spectrometry(UHPLC-FTMS)analyzed colonic metabolite profiles to identify diferential metabolites and asociated pathways.Results Compared with the normal group,the model group exhibited elevated DAI scores ( P<0.001 )and histopathological scores ( P<0.01 ),shortened colon length ( P<0.001 ),and increased IL- 1β and TNF- α levels( P<0.01 and P<0.001 ).Compared with the model group,the XBD high-dose group showed reduced DAI scores( P<0.05 )and histopathological scores( P<0.01 ),longer colon length( P<0.01 ),decreased IL- 1β and TNF -α levels( P<0.05 and P<0.01 ),and significant alleviation of clinical symptoms.Metabolomics revealed that XBD primarily modulated nucleoside-related metabolites and pathways including pyrimidine metabolism, glycerophospholipid metabolism,tyrosine metabolism,and primary bileacid biosynthesis.Conclusion XBD exerts therapeutic efectson UC,potentially mediated byregulating microbial nucleoside metabolism andinfluencing pyrimidine metabolic pathways.
Keywords:Xiaoshi Baitouweng Decoction;ulcerative colitis;metabolomics;nucleoside metabolism;pyrimidine metabolism;mice
溃疡性结肠炎(Ulcerativecolitis,UC)是一种肠道非特异性炎症性疾病,属于炎症性肠病(Inflammatoryboweldisease,IBD)的一种,其重要特征是肠道炎症和肠上皮结构破坏,该病慢性且反复迁延,是结肠癌发病的重要危险因素[-2],因此寻找安全有效的溃疡性结肠炎治疗手段具有重要临床意义。(剩余11109字)