α7nAChR在缺血性脑卒中中的神经保护作用与机制研究进展

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R338.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2097-7174(2025)11-1100-06
DOI:10.3969/j. issn.2097-7174.2025.11.013
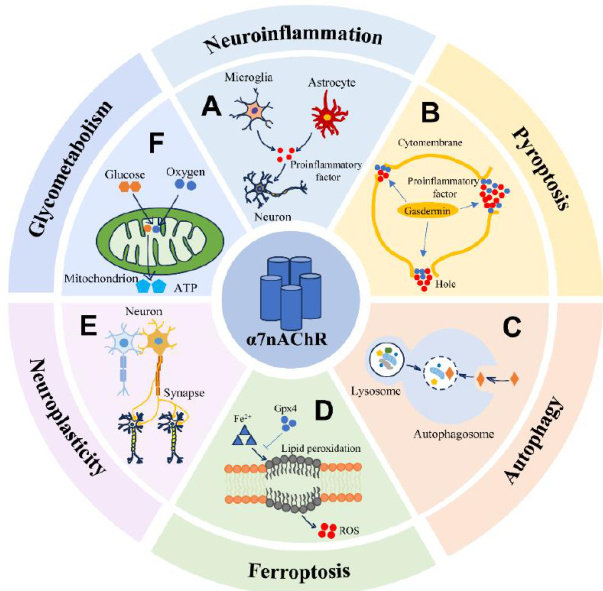
Abstract:Ischemicstrokeisaprevalentcerebrovasculardisorderwithlimitedeffectivetherapeuticinterventions.The α7 nicotinicacetylcholinereceptor(7nAChR),animportantsubtypeofthenon-neuronalcholinergic system,exertspivotal regulatory efects inischemic stroke.Currently,there isalackofcomprehensivesynthesisregardingtheneuroprotective rolesandunderlying mechanisms of α7nAChR in ischemic stroke.This systematic review consolidates recent domestic and foreign literature to elucidate the involvement of ∝/ nAChR across multiple pathophysiological processes in ischemic stroke,includingeuroinflammationpyroptosis,utopagy,erroptosis,uroplasticitymodulationandcrebralglucose metabolism.Theresultsofthe literaturereview indicatethatactivationofα7nAChR post-ischemia promotes cholinergic anti-inflammatorypathways,atenuatesneuroinflammation,modulatesautophagicactivitytopreserveblood-brainbair integrity,inibitsfroptoticcelldath,ducesoxidatiesress,andfcilitatesnti-inflammatoryicroglialpation. These findings highlight α7nAChR asapromising moleculartarget fortherapeutic intervention in ischemic stroke.
Key words: Ischemic stroke;α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor;Physiopathology
脑卒中是全球最主要的死亡原因之一,具有高发病率、高致残率和高死亡率的特点[]。(剩余12919字)