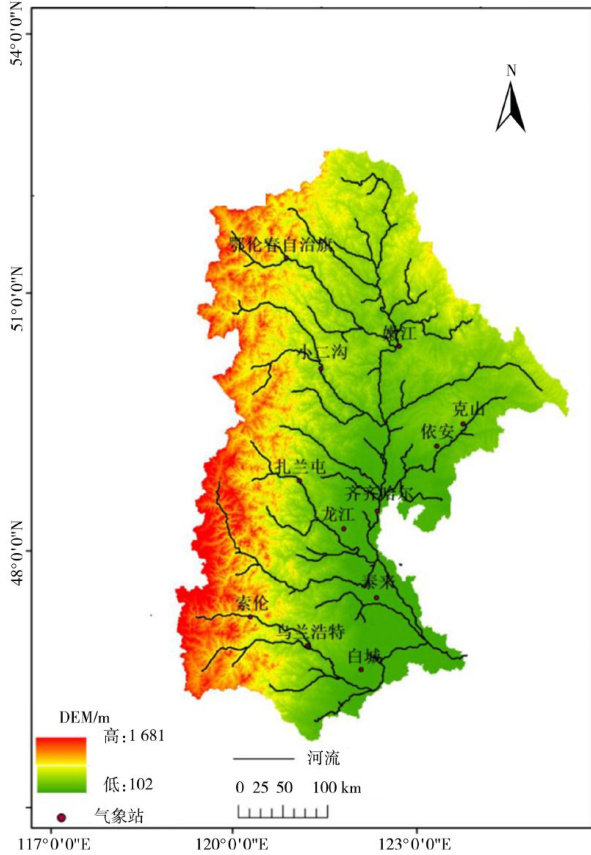
近60a嫩江流域极端气候指数时空分布特征及未来趋势分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TV21 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1001-9235(2025)07-0061-13
Abstract:ThestudyofextremeclimatechangeintheNenjiangRiverBasinisofgreatsignificanceforensuringecologicalsecurityand agriculturalproduction.Basedontheoservationdatasuchasdailytemperatureandprecipitationfrom12meteorologicalstationin theNenjiang RiverBasinbetween196Oand2O20,thispaperselects26extremeclimateindices.Meanwhile,methodslikethelinear fiting,Mann-Kendallutatiost,andsdingttestaedoptedtoaletspatiempralationaractesticftre temperatureandprecipitationinthebasin.Aditioaly,thispaperutilizestheNEX-GDDP-CMIP6datasettopredictfturecliate changetrendsinthbasin.Theresultsshowthatfrom196Oto020,theextremewarmindexsignificantly icreases,whiletheextree coldindexsignfcantlydecreases,withmutationyearsmainlyconcentratedintheyearsafter975.Theextremeprecipitationidex significantlyrises,withmutationyearsprimarilyintheyearsafter2Olo.Intermsofspatialdistribution,theareaswithhighvalue extremecoldindicesaremainlylocatedintheOroqenAutonomousBaner,whiletheareaswithhighvalueextremewarindiesae morescatered.Inadditiontotheintensityindicesotherareaswithhig-valueextremeprecipitationindicsarelsoconcentratedin theOroqenAutonomousBanner.Inthefuture,theNenjiangRiverBasinisexpectedtoshowawarmingtrendintemperatureanda risingtrendinprecipitation,withanicreasedprobabilityofextremehigh-temperatureeventsandextremeprecipitationevents. Keywords: extreme climate index;spatio-temporalcharacteristics; NEX-GDDP-CMIP6;future trends;Nenjiang River Basin
近年来,随着全球气候变化,极端气候变化已成为全球关注的焦点,特别是极端气候事件,不仅对自然环境构成威胁,对人类和社会经济的危害也更大[1-5]。(剩余13532字)