漂浮物对城市道路雨水口致堵规律研究

打开文本图片集
Abstract:Toinvestigatetheimpactofdiferentfloatingdebrisonthedrainageperformanceofurbanpipenetworksystemsystems,this studyconductedaseriesofphysical modeltestsbasedonslope experiments byconsidering thedrainageprocessofthe pipenetwork. Theeffectsofvaryingsurfaceslopes,storm-waterinletclogging,andtypicalfloatingdebriscloggingontheperformanceofthepipe network system were examined. The results show that: ① Under four clogging conditions on a flat slope,the drainage capacity of the storm-water inlet decreases by 21.45 % ~27.43 % ,37.59 % ~65.25 % ,10.69 % ~24.61 % ,and25.66 % ~58.96 % compared to the clogging-free condition. ② At lower flow rates,even though theclogging area offloating debris is small,the flow rate of the drainage pipenetwork during clogging of the storm-water inlet by typical floating debris decreases by 5.64 % ,16.38 % ,13.67%,and 37.48 % (204号 comparedtothcloggingfreecondition.Thisindicatesthatthereductionindrainagecapacityiselatedtotheobstructioncausedby floating debris upstream of the storm-water inlet. ③ When the storm-water inlet has 60% clogging at three different slopes,the flow rates of the drainage pipe network decrease by 15.86 % ,12.33 % ,and 29.61% ,respectively. The slope of the road also has a significant impact on the discharge capacity of the storm-water inlet. ④ The degree of impact of different floating debris on the drainagesystemvariessignificantlyunderdiferentslopes.Theresearch findingsprovideanempiricalbasisforthedesignand evaluationofurbandrainagesystems,whichisofgreatsignificanceforenhancingthefloodpreventioncapabilitiesofurbandrainage systems and responding to extreme weather events.
eyWords:storm-waterinlet;storm-waterinletclogging;typicalfloatingdebris;simulateddrainage test;flooddisaste
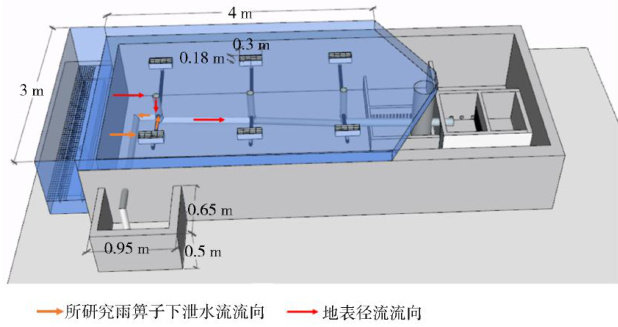
近年来,中国城市内涝的频发,极端降雨事件日益常见,不仅加剧了地表水径流的排放压力,更对人民的生命财产安全构成了严重威胁[1-2]。(剩余8603字)