CoCu双原子驱动的高效电催化甲烷制甲醇

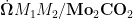
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:0643 文献标志码:A
Abstract:Thefirst-principlesdensityfunctionaltheorycalculationswasusedtoivestigatetheperformanceofdual-atomcatalysts(DACs)anchored on a Mo2CO2 MXene substrate(denoted as M1M2/Mo2CO2 ,where M1=Fe,Co,Ni and M2=Co , ΔNi,Cu) for the electrocatalytic conversion of methane ( CH4 )tomethanol( CH3OH ).The stability of the catalysts was assessedviaformationenergyanddisolutionpotentialcalculations.Thecatalyticactivityandselectivitywereprobedthrough reactionfreeenergyanalysis.Theoriginofcatalyticactivitywas elucidatedviaelectronicstructureanalysis.Itisfoundthat the formation energy of M1M2/Mo2CO2 catalyst is from -4.44eV to -2.62eV ,and the dissolution potential is between 1.03 V and 1.77V ,exhibiting excellent thermodynamicand electrochemical stability.Among them,the activation energy barrier of methane on CoCu/Mo2CO2 is only 0.05eV ,indicating excellent catalytic activity.Within a potential windowof 0.74V to 1.01V (vs.RHE),this catalyst achieves methanol selectivity exceeding 99% .Thecatalytic activity shows a positive correlation with the charge ratio (q(M1)/q(M2)), )of the dual-metal centers.The high activity of CoCu/Mo2CO2 originates from its q(M1)/q(M2) ratio of O.3,which is close to the theoretical optimumvalue.
Keywords:first principles;methane to methanol;diatomic catalysts;electrocatalysis
甲烷作为重要的化学原料之一,是许多化学品生产的基础,且可以通过天然气、页岩气等方便获得[1-3]。(剩余13951字)