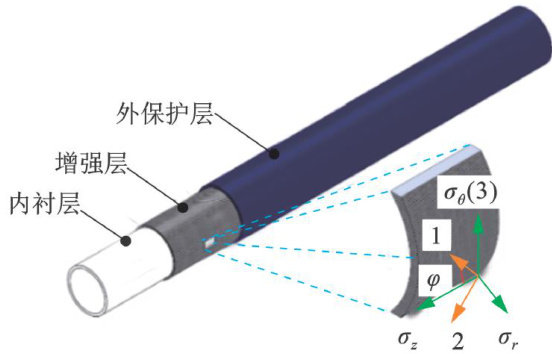
纤维增强热塑性管道熔接补强接头爆破失效机制

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TE952 文献标志码:A
Abstract:Toaddressthecuentchallngesofcoosionsuseptibityfatiguevulnerability,andexcessiveouterdiameterin fiber-reinforcedthermoplasticpipes(RTPs)connection joints,thisstudydesignedanovel fusion-reinforced jointbasedon theoreticalmodeling.Amethodologycombiningfiniteelementsimulationsandbursttestingisemployedtosystematicallyinvestigatethefailure mechanismsoffusion-reinforced jointsofRTPsunderburstloadingconditions.Theprogressivedamage evaluationmethodbasedontheVUMATsubroutinewasdevelopedbycombining the3DHashinfailurecriterionwiththemaximumstresscriterion,andintegratingresidualstiffess modelingandcohesivezonemodeling.Experimentaland numerical resultsdemonstratethattheultimatefailuremodeis thefailureoftheadhesivelayerandthefusionzone.Thedamage evolutionprocessprogresesthroughfourdistinctstages,namelytheinitialudamagedstage,theadhesivelayerdamagestag,the matrixdamagestage,andthefinalcatastrophicfailurestage.Thedamageoftheadhesivelayerspreadsfrombothendsof the jointtowardsthecenter,withinsufficientshearstrengthoftheadhesiveinterfaceidentifiedastheprimarycontributingfactor. Matrixdamage intheRTsreinforcementlayerinitiallyoccursadjacenttothejointinterfaceandprogressvelyextendstononjointregions.The matrixdamage in the jointarea is influenced bythe expansion lawof theadhesive layer damage
Keywords:reinforced thermoplastic pipes;joint design;progressive damage;burst failure;cohesive zone mode
纤维增强热塑性管道作为新型非金属复合管,兼具高强度、耐腐蚀及柔性输送优势,已逐步开始应用于海洋与陆上油气田[1-2]。(剩余12354字)