非均质出砂水平井产液剖面演化及热点形成机制试验

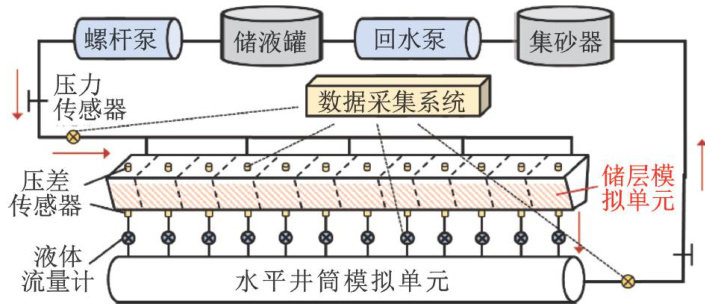
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TE358 文献标志码:A
Abstract:Inthisstudy,simulationexperimentswereconductedtostudytheevolutionoffluid inflowprofilesandtheformationmechanismofhotspots innon-homogeneoussandproductiohorizontalwellsusingalarge-scalehorizontalwell testingequipment.Threenon-homogeneous reservoirrock models wereconstructed byanartificiallycementing method.Theexperimentalresultsshowthatfluidandsandproductioncanexhibitasynergisticeffect,withthediferenceofsand-outintensity betweenstronglyandweaklyconsolidatedreservoirregions increasingwith thefluidproduction.Eventuall,thesandproductionprofiledistributionisiversetotheinitialcompresivestrengthdistribution,resemblingtheinitialrockporosityandper meabilitydistribution.Undertheinfluenceofthesand-fluidsynergsticproductionmechanism,localhighrateinflowhotspots may emerge after long production periods.The experiments reveal that a hotspot area can contribute over 80% of the total fluid production.Duetotheformationofhigh-rateinflowhotspots,theinflowcoeficientinlowconsolidationstrength/highporosity/highpermeabilityregionscanincreasefromaninitialrangeofO.2-O.4tooverO.8.Meanwhile,thepermeabilitydistributionofthereservorcanshiftfromaninitialgradualvariationalongthehorizontalwelltoaighlyheterogeneousdistribution,with thevalues ofpermeability increasingbyup to17.5 times.
Keywords:non-homogeneousreservoir;losesandstonereservoir;horizontal wellsandproduction;inflowhotspot;sand-fluid production profile;synergistic effect
疏松砂岩储层是中国油气增储稳产的关键领域,水平井技术是其高效开发的核心手段。(剩余13122字)