CO2注入提高深部煤层气采收率多因机制试验

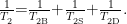
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TE357.7 文献标志码:A
Abstract:Inthisstudy,thefieldinjectionandproductionprocessweresimulatedusinganonlinevisualnuclearmagnetic resonance(NMR)technique to investigate CO2 -enhanced coalbed methane recovery( CO2 -ECBM)through physical experiments,and the impacts pressure,temperature,injection volume,water saturation,and pore characteristics on CH4 desorption and displacement were analyzed.The results indicate that increasing injection pressure from 10MPa to 20MPa can reduce CH4 adsorption capacity by 32.6% ,demonstrating a significant role pressure on enhancing the competitive adsorption CO2 .Temperature elevation can linearly decrease CH4 adsorption by 30% ,while higher CO2 injection volume can reduce CH4 desorption by 27.6% ,conforming to a linear relationship.Additionally,increased water saturation can reduce CO2 (204号 displacement efficiency,with a decline in CO2 adsorption capacity as water saturation increases,indicating that occupation adsorption sites by water molecules inhibits thegas displacement process.Larger pore diameters can enhance CH4 adsorption capacity,and CO2 displacement eficiency can be improved progressively as pore size increases.The experimental results confirm the preferential adsorption supercritical CO2 in deep coal seams,which is governed by multifactorial coupling mechanisms.
Keywords:supercritical CO2 ; CH4 ;NMR technology;competitive adsorption;unit adsorption capacity
二氧化碳( CO2 )是一种强效的温室气体,过量的 CO2 排放对人类生存和地球环境构成威胁。(剩余17298字)