毛乌素沙地植被恢复状况多指标遥感监测

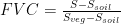
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S154 文献标识码:A 文章编号:0488-5368(2025)09-0094-08
Abstract: The Mu Us Sandy Land,one of China' four major sandy areas,has achieveda historic transformation from“sand advancing and people retreating”to“green advancing and sand retreating” in recent years, owing to global climate changeand the implementationof policiessuchas"returning farmland to forests and grassands".As a result,vegetation conditions in the region have significantly improved.This study takes the Mu Us Sandy Land as the research area,and,byapplying remote sensing and GIS technologies,selects multiple indicators including the Normalized Diffrence Vegetation Index (NDVI),Fractional Vegetation Cover(FVC), and Net Primary Productivity(NPP)to monitor vegetation restoration from four aspects:spatial distribution, magnitude of change,trend of change,and stability.The results showed that:(1)From 2O0O to 202O,the NDVI in the Mu Us Sandy Land increased at arate of 0.75% per year, indicating significant vegetation restoration. (2)The spatial distribution of FVC exhibited significant variation,with vegetation coverage generally decreasing from southeast to northwest.The proportion of bare land continued to decline,while the proportion of medium - to high-vegetation coverage areas steadily increased.Over the past two decades,vegetation coverage has continuously expanded and improved markedly.(3)From 20O to 2O16,the NPP index increased significantly,with growth in the southeast being more pronounced than in the northwest,indicating a notable improvement in vegetation productivity.The trends reflected across the NDVI,FVC,andNPP indicators from 2OOO to 2020 were consistent,showing that the vegetation in the Mu Us Sandy Land had been clearly and continuously recovering.
Key words: Mu Us Sandy Land; Vegetation coverage; Net primary productivity;Spatiotemporal variation
1引言
2 研究区域与研究方法
沙漠化是一种常见的土地退化类型,早在上世纪九十年代,就引起全球性的普遍关注[1~3]。(剩余9886字)