施肥模式对旱地大豆生长发育及产量构成的影响

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S565.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:0488-5368(2025)09-0054-06
Abstract: To investigate the efects ofcombined nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) fertilizers as well as the biochar application on the physiological regulation,root morphologyand yield components of dryland soybean,an experiment was conducted using the cultivar Zhonghuang 13'as as test material.Four fertilization treatments were set up:CK (N, 30kg/hm2 ),DNP(N, 60kg/hm2 ,P, 30kg/hm2 ),GNP(N,90 kg/hm²,P, 45kg/hm2 ) and GNP -C(N, 90kg/hm2 ,P, 45kg/hm2 ,Biochar, 1500kg/hm2 ),to analyze how different fertilizer combinations affect root morphology,agronomic traits,and yield in dryland soybean.The results showed that:(1) relative to CK,soybean yield increasedby an average of 42.85% across fertilized treatments,and the yields under GNP -C,GNP,and DNP increased significantly by 58.31% , 45.82% ,and 24.42% ,respectively;(2) chemical fertilizer combined with biochar significantly promoted root growth and development;under GNP-C, root length and root surface area increased by 37.64% and 35.29% ,respectively,and root volume increased by51.09% ,thereby enhancing the plant’s root - system functioning and providing potential for yield improvement; (3)the combination of chemical fertilizer and biochar effectively promoted rational biomass allocation,with the GNP - C treatment showing a 73.35% increase over CK,the highest among treatments;and (4) the dry weight of soybean roots and aboveground parts followed an S-shaped curve,peaking at the full bloom and seed -filling stages,respectively.In conclusion,the GNP-C treatment improves the spatial distribution of the root system, enhances dry-mater accumulation and allocation,balances biomassalocation,and supports high,stable yield. atter accumulation and allcation,balances biomass alocation,and supports high and stable yield.
Key Words: Biochar; Loess dryland; Morphological development; Physiological function; Root morpholog
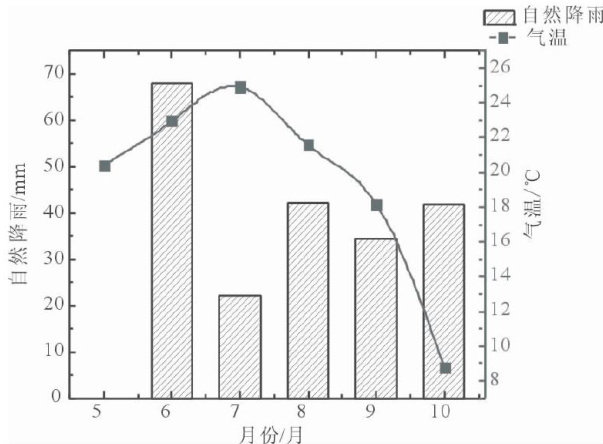
我国耕地质量逐年下降,农田生态系统破坏严重。(剩余7513字)