外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下小麦幼苗生理特性的影响

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S512 文献标识码:A 文章编号:0488-5368(2025)09-0008-06
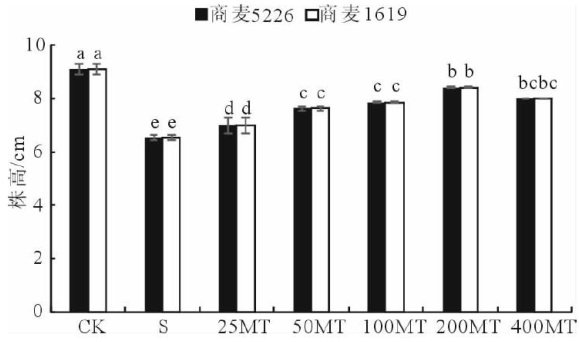
Abstract:To clarify the physiological effects melatonin at optimal concentrations on enhancing salt tolerance in wheat seedlings,the wheat cultivars‘Shangmai 5226’‘Shangmai 1619’were used as experimental materials. Treatments included a control(CK),25O mmol/L NaCl solution(S),S + 25 μ mol/L melatonin (25MT),S + 50 μmol/L melatonin (50MT),S + 100 μmol/L melatonin(100MT),S + 200 μ mol/L melatonin(200MT), ΔS+400μmol/L melatonin (4OoMT). The effects melatonin on growth physiological characteristics were evaluated under salt stress.The results showed that all melatonin treatments (25~ 400μmol/L ) improved the growth physiological characteristics wheat seedlings under salt stress to varying degrees.The 2OOMTtreatment significantly increased plant height,root length,dry weight,fresh weight, root-to-shoot ratio,as wellas chlorophyll content,soluble sugar content,peroxidase (POD)activity, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity,while significantly reducing malondialdehyde(MDA) proline content in both cultivars. These findings indicate that 200 μmol/L melatonin effectively alleviates the adverse effects salt stress represents an optimal concentration for promoting wheat seedling growth under such conditions.
Key Words: Salt stress;Wheat seedlings;Melatonin; Growth indexes;Physiological indexes小麦与稻谷和玉米共同构成了世界三大主要 谷物。(剩余8610字)