考虑地形影响和震源动力学过程的2021年漾濞Ms6.4地震强地面运动数值模拟

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P315 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-0844(2025)06—1457—13
DOI:10.20000/j.1000-0844.20231012006
Abstract: The 2021 Yangbi Ms6.4 earthquake in Yunnan Province is the strongest seismic event in the region in recent years and has generated intense strong ground motions that caused significant casualties and property damage. Numerical simulations were conducted on the strong ground motion to deepen the understanding of its characteristics. A 3D geological model incorporating actual topography and a fault weakening model with elastic material properties were used to simulate dynamic rupture. Results demonstrate that the rugged topography of the Hengduan Mountains considerably influences the strong ground motion distribution of the Yangbi earthquake,with an amplification effect at the ridges and steep slopes where the elevation changes abruptly. When preseismic stress fields are introduced through boundary conditions and variations in fault material strength before and after the earthquake are considered,the simulated strong ground motion-including its magnitude, distribution,and attenuation rate-closely approximates the actual event. Simulated results of peak ground acceleration (PGA) and acceleration response spectrum at near-field stations align closely with the observational records. PGA contours correspond closely to the seismic intensity maps in spatial distribution. Integrating realistic topography with dynamic source modeling can enhance the simulation reliability for seismic hazard mitigation and resilient urban planning.
Keywords: Yangbi earthquake;dynamic source model; strong ground motion; finite element simulation; peak ground acceleration
0 引言
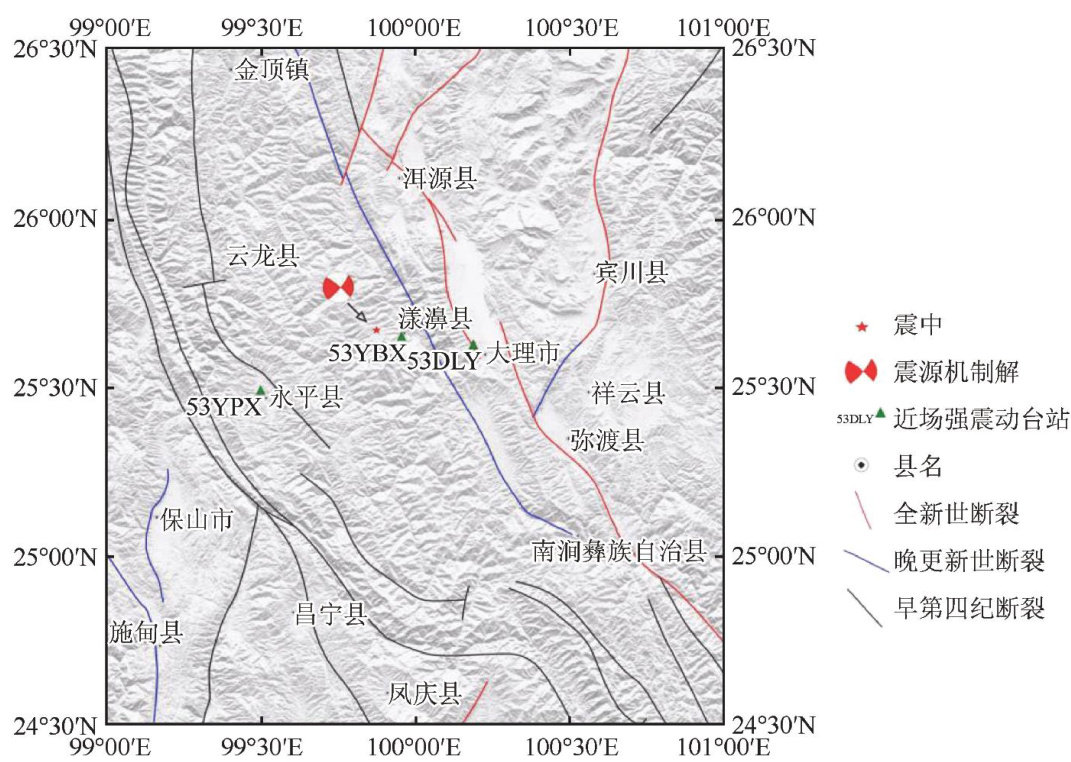
2021年5月21日21时48分34秒,云南省漾濞县 (25.67∘N,99.87∘E) 发生 Ms6.4 地震,震源深度约9km[1] 。(剩余18598字)