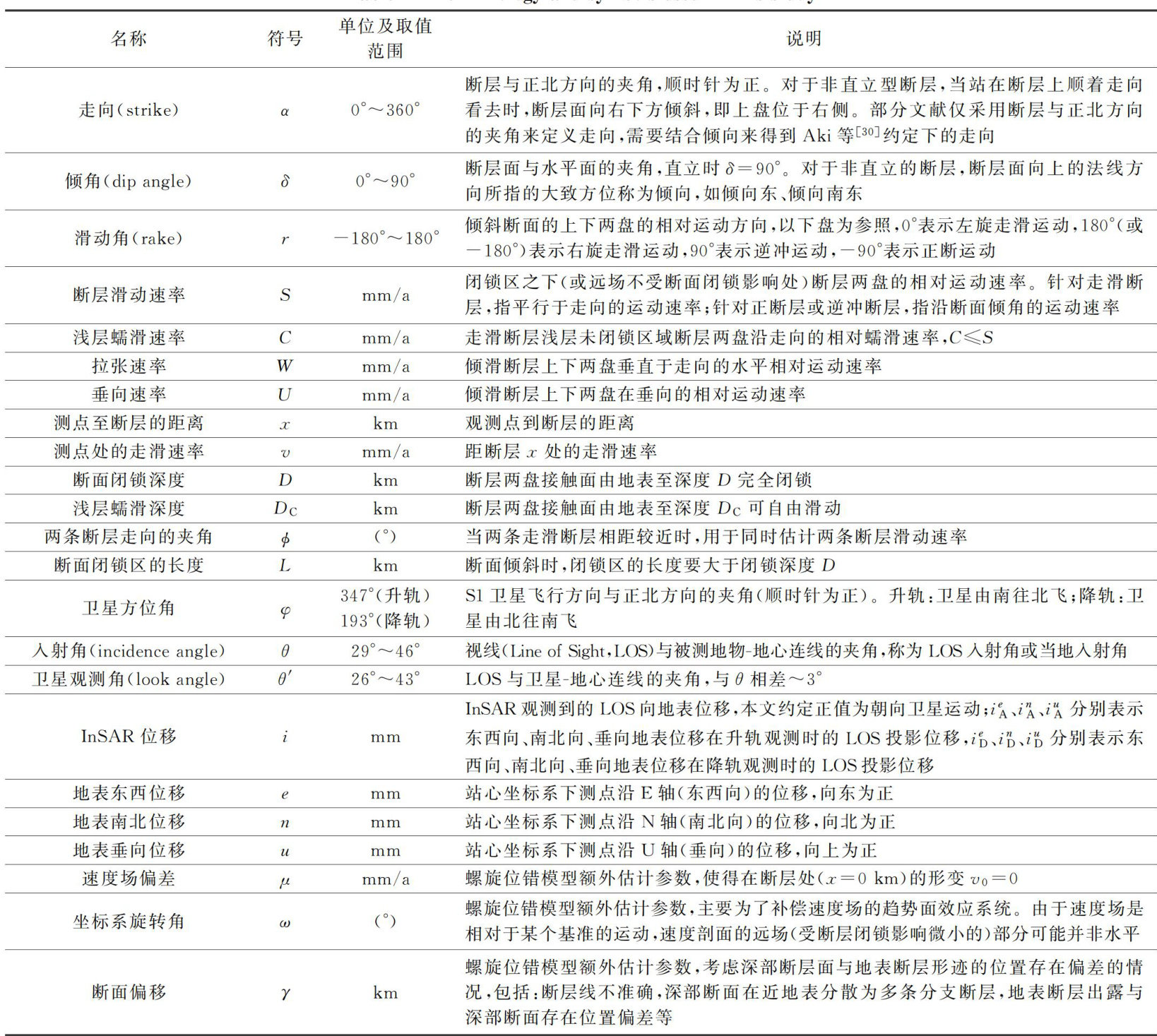
利用InSAR探测活断层现今运动的方法概述

打开文本图片集
关键词:合成孔径雷达干涉测量;活断层;螺旋位错模型;滑动速率;哨兵1号中图分类号:P315 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-0844(2025)06—1399—17DOI:10.20000/j.1000-0844.20230816001
Abstract: Crustal movement information with millimeter-scale measurement accuracy, obtained through synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR) technology,is crucial for assessing the seismic risk of active faults. This technology involves several fields, such as earthquake geology, geophysics, geodesy, and remote sensing. Thus, researchers from various fields need to acquire a foundational understanding of the necessary professional knowledge when applying this technique. This paper first systematically presents an introduction to the basic knowledge of seismology and geophysics,including active faults and earthquakes.Given the unique characteristics of crustal deformation monitoring using radar satellites, the paper then discusses the satelite observation geometry and explains the conversion between line-of-sight deformation and three-dimensional crustal movement/fault movement. The paper also highlights the limitations of space-borne InSAR technology in monitoring strike-slip fault movements with varying strike orientations. The inversion methods for estimating slip rates of active faults using deformation profiles were summarized.These methods include the screw dislocation model (SDM) and earthquake cycle model for strike-slip faults,the edge dislocation model for dip-slip (normal/thrust) faults,as well as the variants of the SDM that include other factors, such as the asymmetric and shallow creep models. These analytical and semi-analytical models have been widely used in the study of active faults due to their simplicity, ease of implementation,and high accuracy. Finally,the paper discusses the influence of non-tectonic signals in the InSAR deformation field and highlights the problems that need attention in practical applications. This work provides valuable insights for readers to better understand the current methods and knowledge related to monitoring active fault movement using InSAR. The findings are of considerable value for earthquake prevention and disaster reduction efforts,such as regional earthquake risk analysis.
Keywords: interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR);active fault; screw dislocation model;slip rate;Sentinel-1
0 引言
受欧亚与印度、太平洋等板块碰撞的影响,活动断层在我国内陆和沿海广泛发育,在历史上曾多次发生破坏性大地震,如1556年华山山前断层上的陕西华县 Mw8.0 地震、1920年海原断层上的宁夏海原 Mw8.3 地震、1976年唐山断层上的河北唐山Mw7.6 地震,累计造成了上百万人遇难。(剩余37405字)